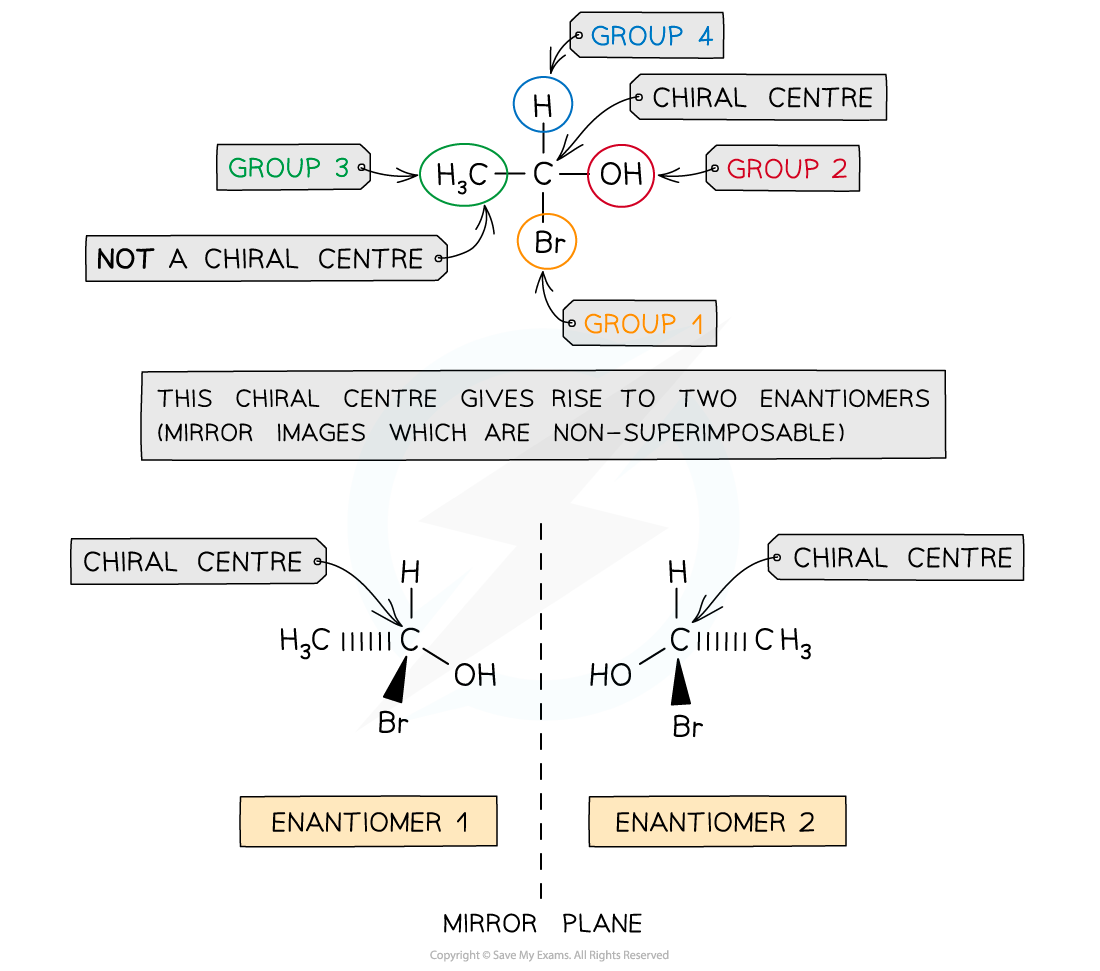
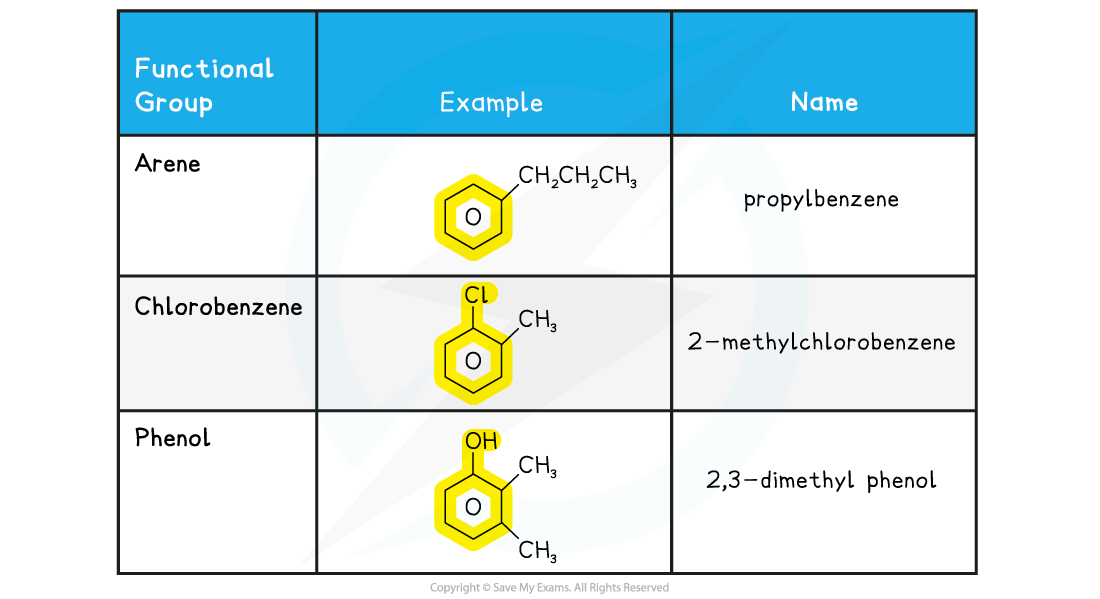
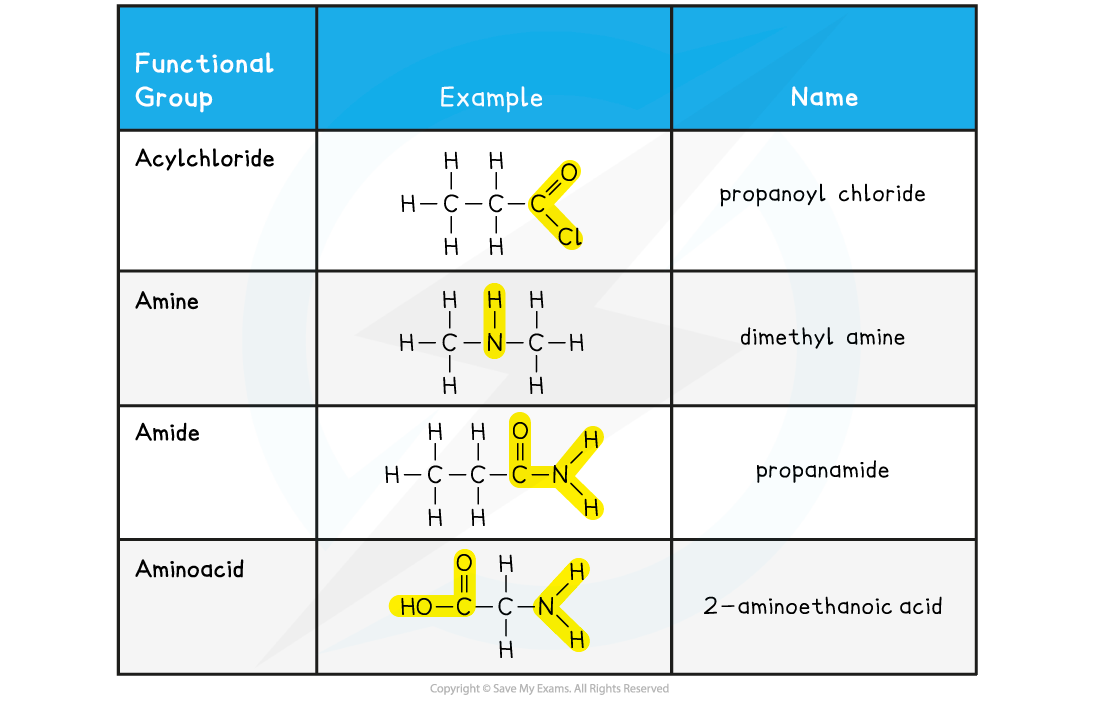
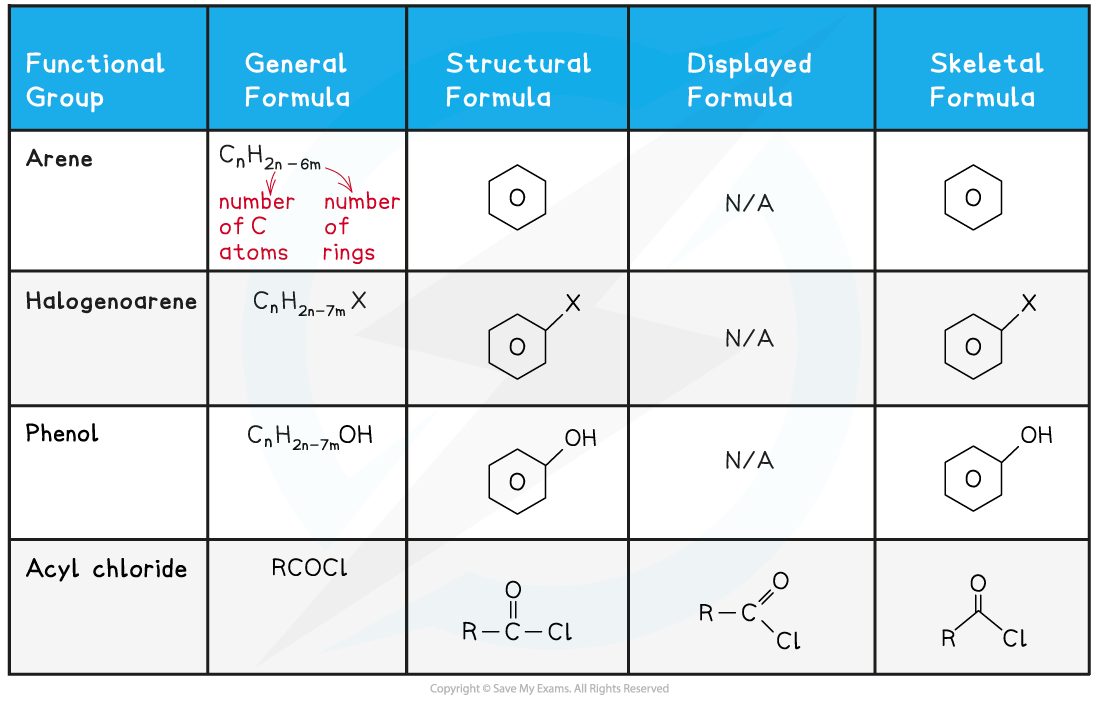
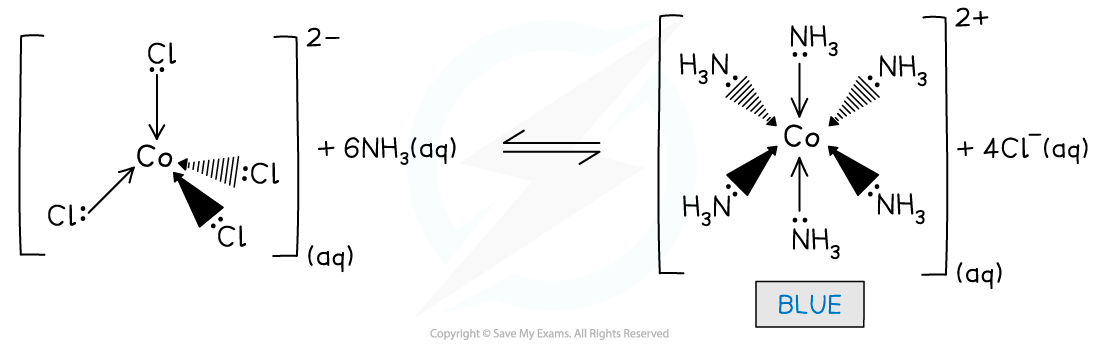
CIE A Level Chemistry复习笔记7.2.1 Reactions of Arenes
Reactions of Arenes Arenes are very stable compounds due to the delocalisation of π electrons in the ring This is because the negative charge is spread out over the molecule instead of being confin...