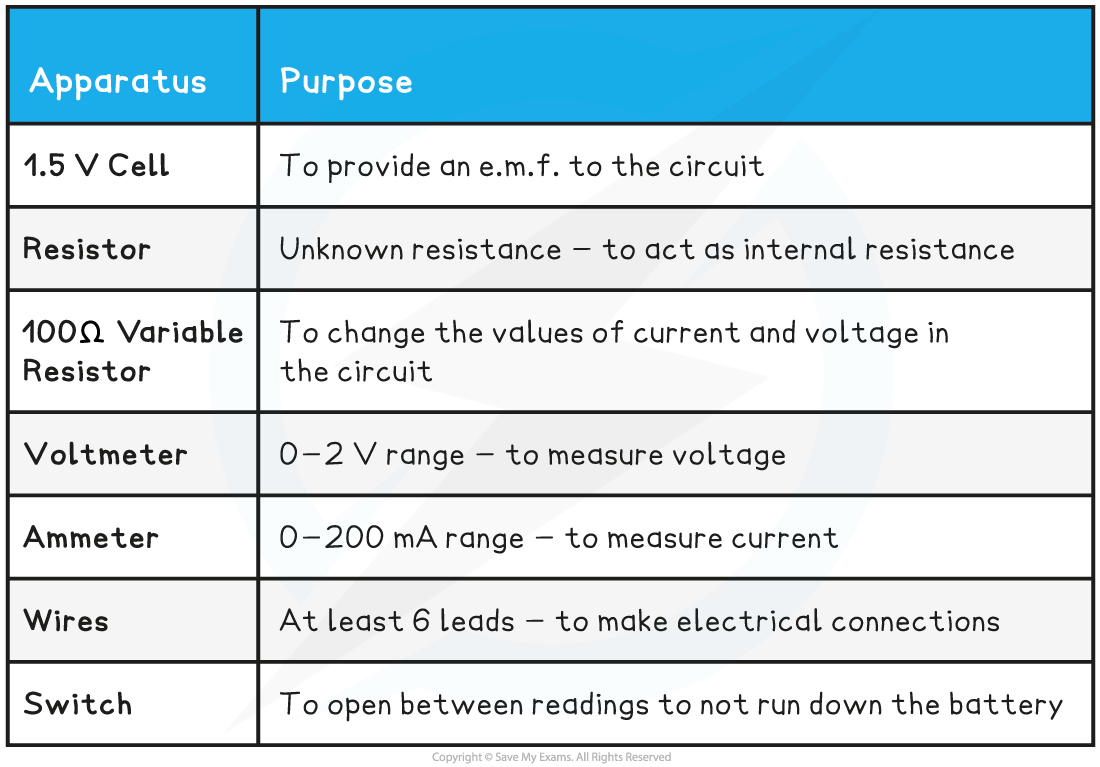
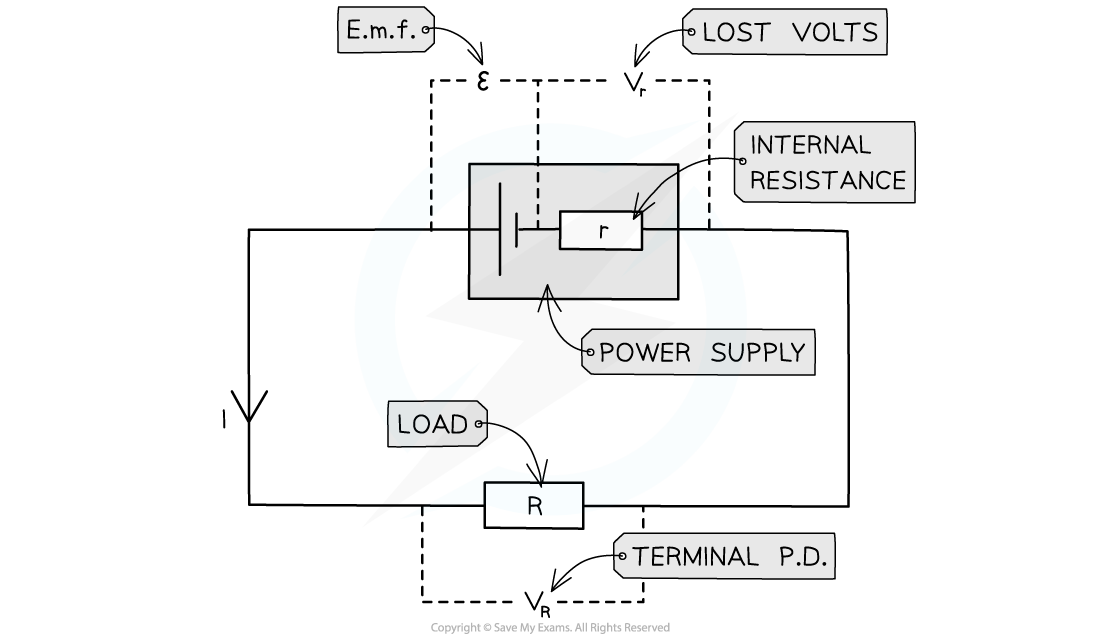
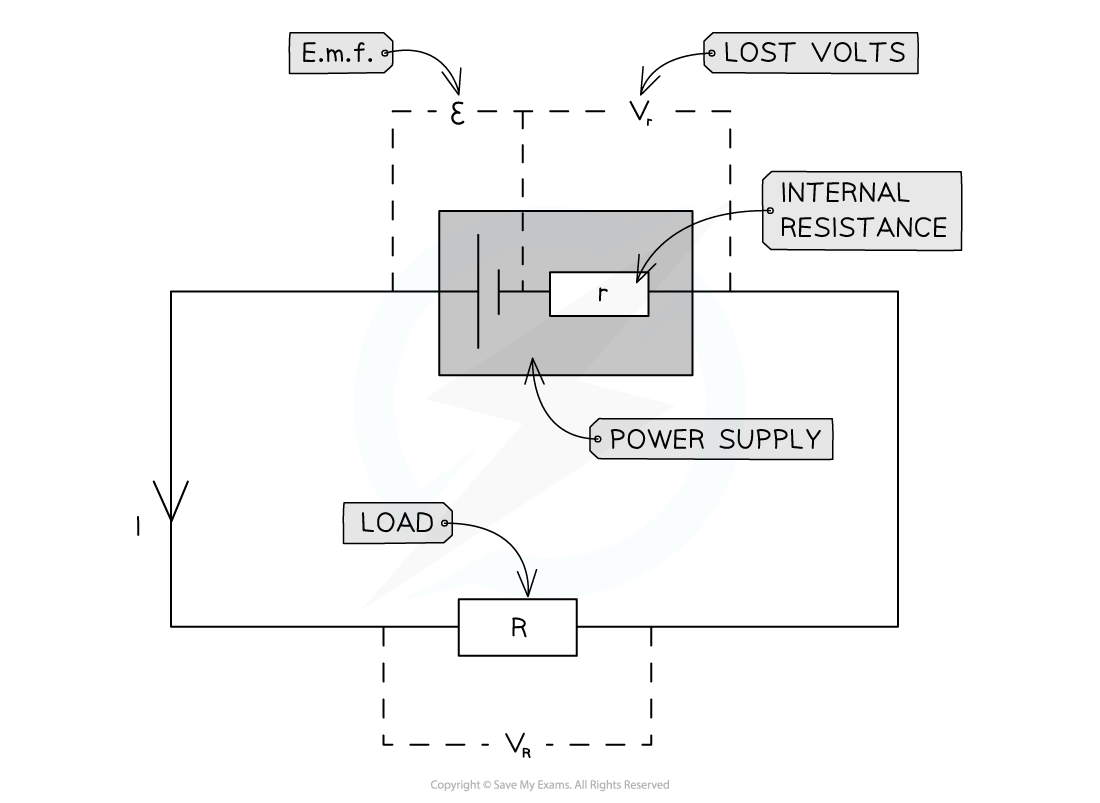
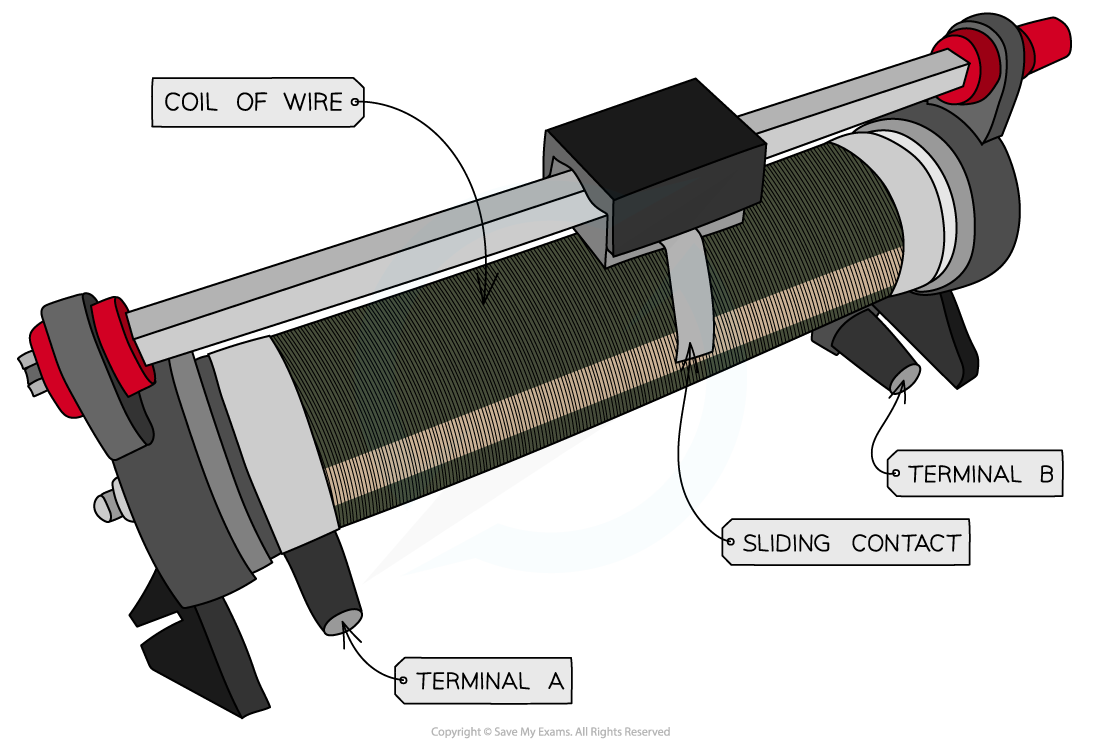
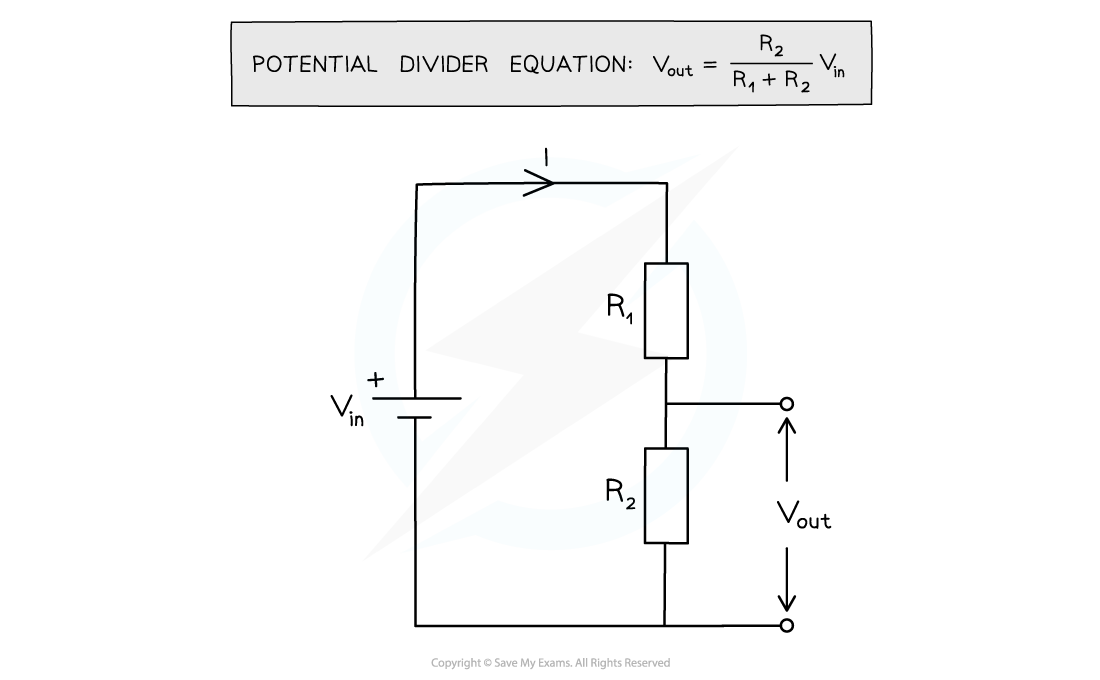
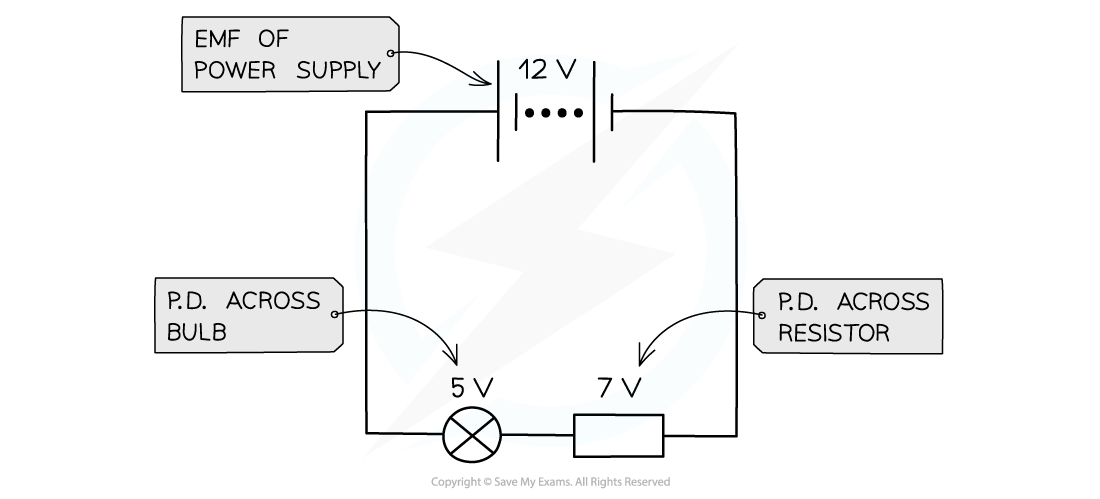
Edexcel A Level Physics:复习笔记3.19 Resistance & Temperature
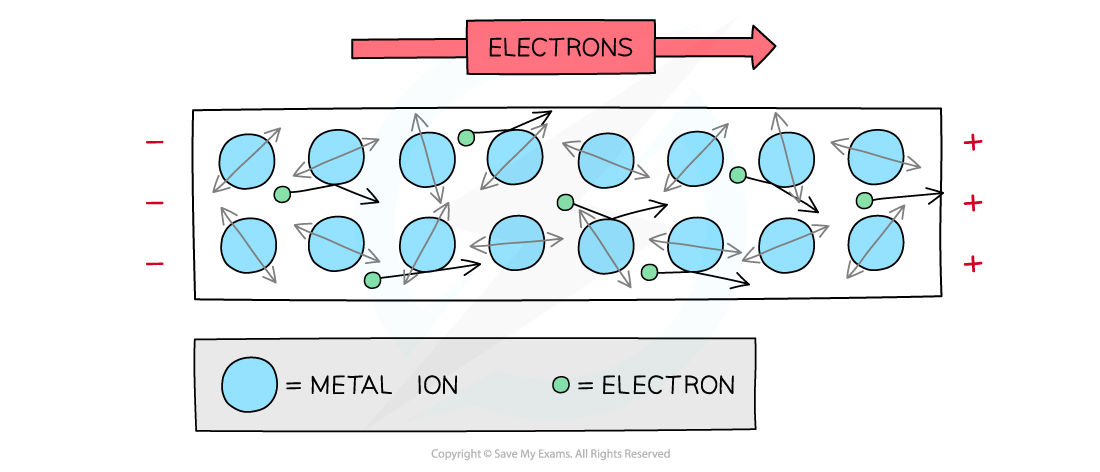
Modelling the Variation of Resistance with Temperature All materials have some resistance to the flow of charge As free electrons move through a metal wire, they collide with ions which get in thei...