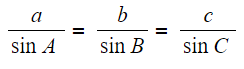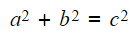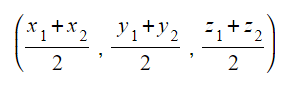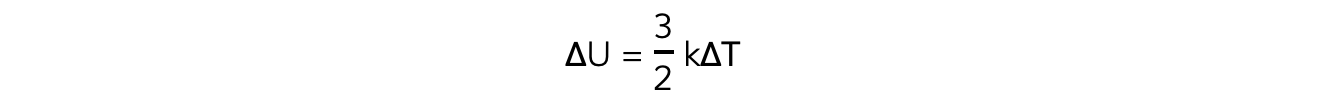IB DP Maths: AA HL复习笔记3.3.3 Applications of Trigonometry & Pythagoras
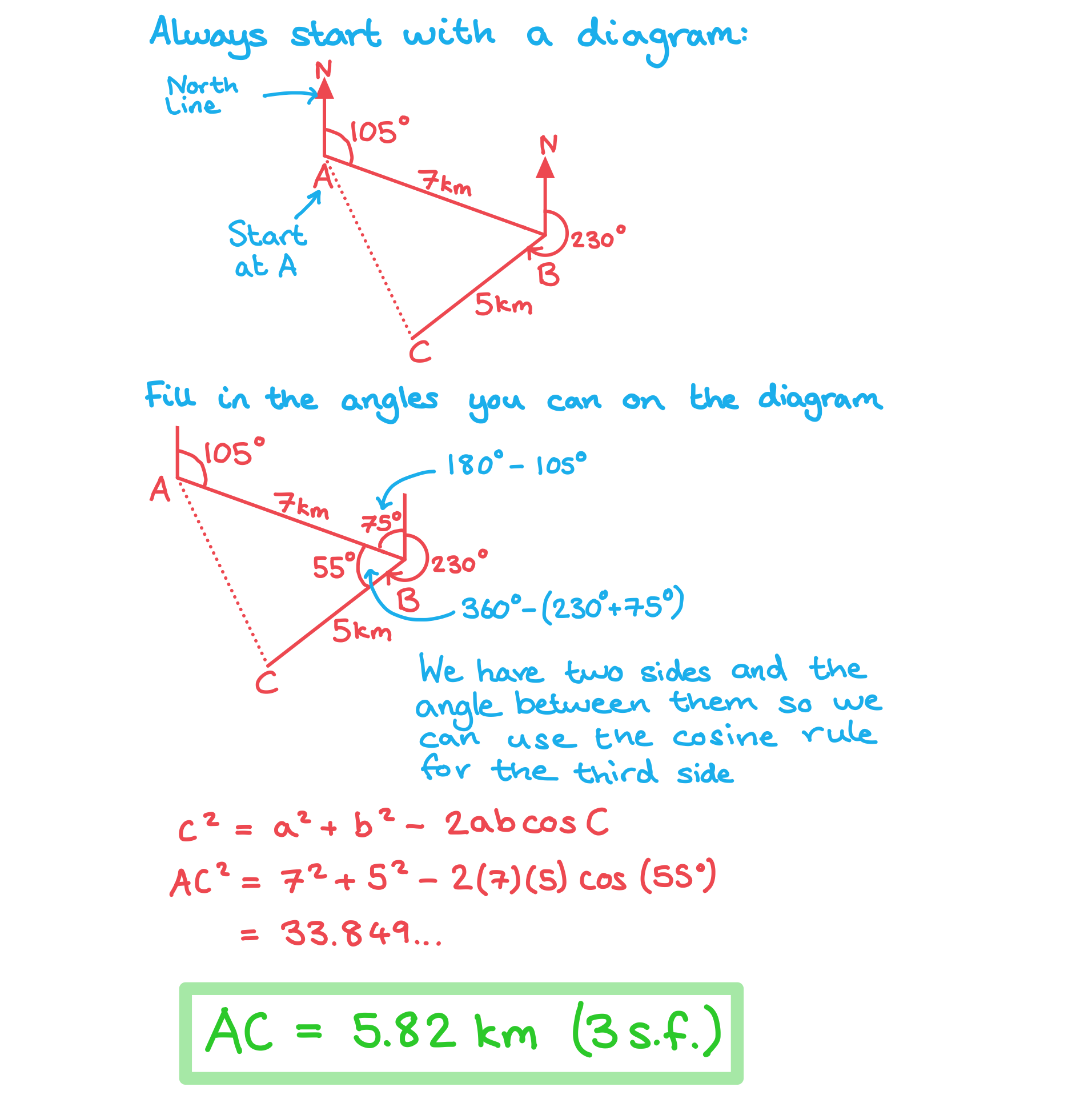
Bearings What are bearings? Bearings are a way of describing and using directions as angles They are specifically defined for use in navigation because they give a precise location and/or direction...