IB DP Chemistry: HL复习笔记16.2.2 Graphing the Arrhenius Equation
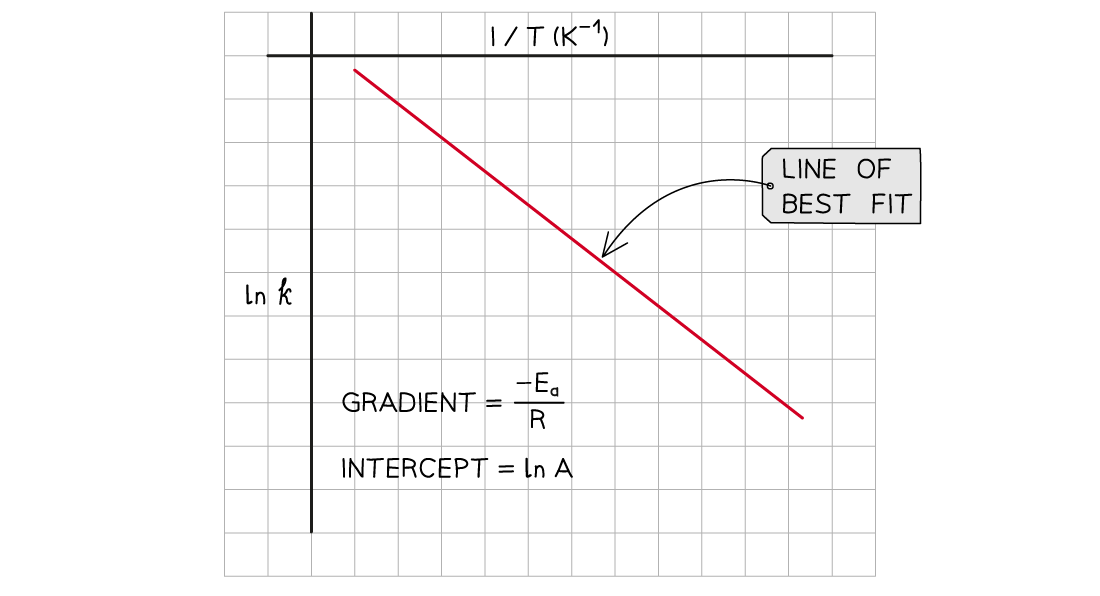
Graphing the Arrhenius Equation Finding the Activation Energy Very often, the Arrhenius equation is used to calculate the activation energy of a reaction A question will either give sufficient info...