- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Chemistry: SL复习笔记3.1.6 Periodic Trends: Chemical
Metallic & Non-metallic
- Periodic trends can also be seen in the typical properties of metals and non-metals which are summarised below:
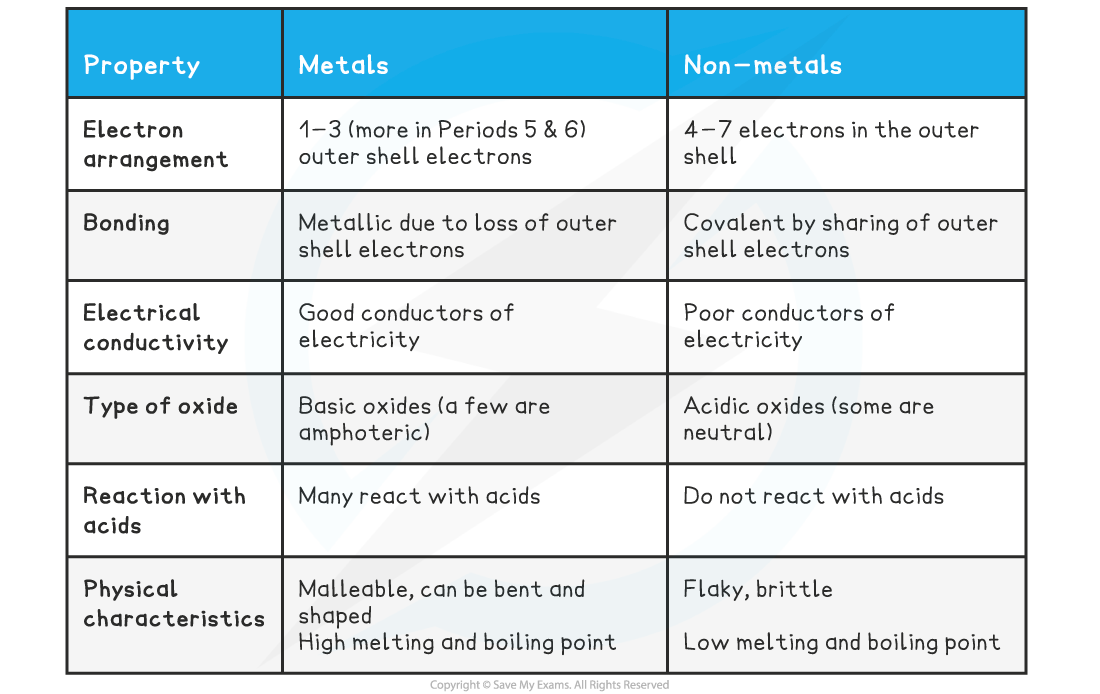
The typical properties of metals and non-metals
- The typically properties of metals and non-metals can be explained by reference to their trends in atomic radius, ionic radius, ionisation energy, electron affinity and electronegativity
- The low ionisation energies and low electronegativities of metals can account for the ability of their valence electrons to move away from the nucleus
- This is known as 'delocalisation' of the electrons
- These properties increase from left to right as you transition from metal to metalloid to non-metal
- The high electronegativity and electron affinity of non-metals can be related to their tendency to share electrons and form covalent bonds, either with themselves or other non-metal elements
- The similarities in electronegativities of the diagonal band of metalloids which divides the metals from the non-metals explains the behaviour of metalloids
Test yourself on the trends in the periodic table:
Worked Example
Which increase across a period from left to right?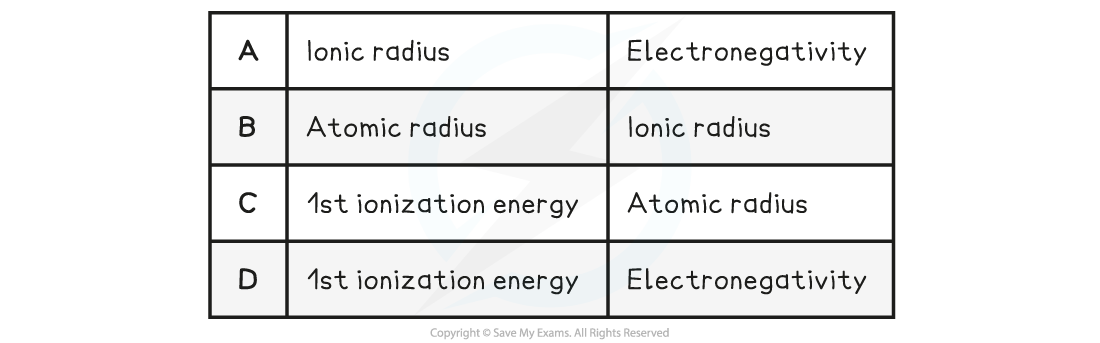
Answer:
The correct option is D
-
- Across a period atomic radius decreases, electronegativity and ionisation energy increase and ionic radius increases then decreases
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









