- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Maths: AA HL复习笔记4.7.1 Probability Density Function
Calculating Probabilities using PDF
A continuous random variable can take any value in an interval so is typically used when continuous quantities are involved (time, distance, weight, etc)
What is a probability density function (p.d.f.)?
- For a continuous random variable, a function can be used to model probabilities
- This function is called a probability density function (p.d.f.), denoted by f(x)
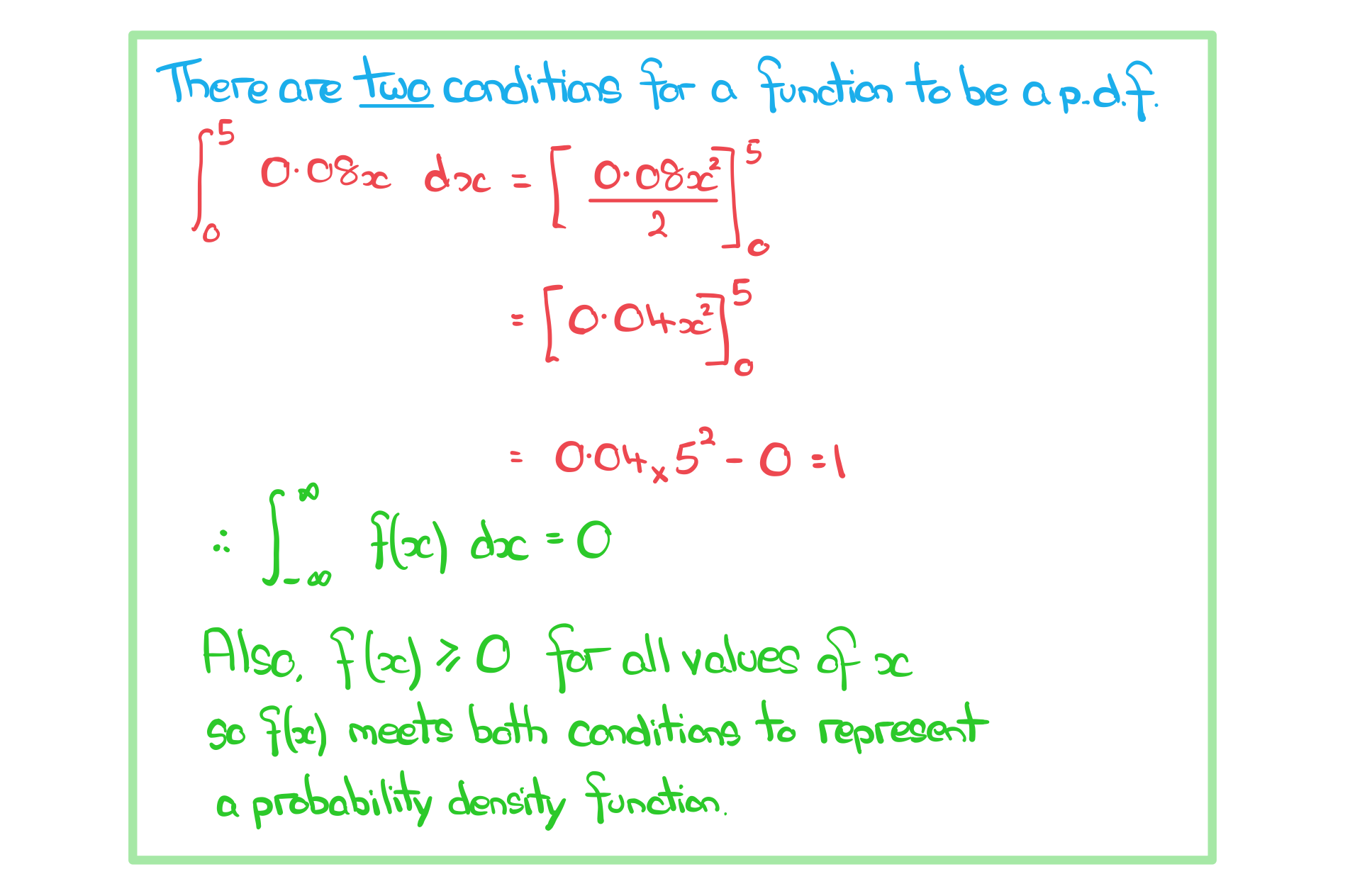
- For f(x) to represent a p.d.f. the following conditions must apply
- f(x) ≥ 0 for all values of x
- The area under the graph of y = f(x) must total 1
- In most problems, the domain of x is restricted to an interval, a ≤ X ≤ b say, with all values of x outside of the interval having f(x)=0
How do I find probabilities using a probability density function (p.d.f.)?
- The probability that the continuous random variable X lies in the interval a ≤ X ≤ b, where X has the probability density function f(x), is given by
-
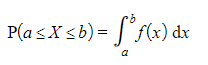 P(a ≤ X ≤ b) = P(a < X < b)
P(a ≤ X ≤ b) = P(a < X < b)
- For any continuous random variable (including the normal distribution) P(X = n) = 0
- One way to think of this is that a = b in the integral above
- For linear functions it can be easier to find the probability using the area of geometric shapes
- Rectangles: A = bh
- Triangles: A = ½(bh)
- Trapezoids: A = ½(a+b)h
How do I determine whether a function is a pdf?
- Some questions may ask for justification of the use of a given function for a probability density function
- In such cases check that the function meets the two conditions
- f(x) ≥ 0 for all values of x
- total area under the graph is 1
- In such cases check that the function meets the two conditions
How do I use a pdf to find probabilities?
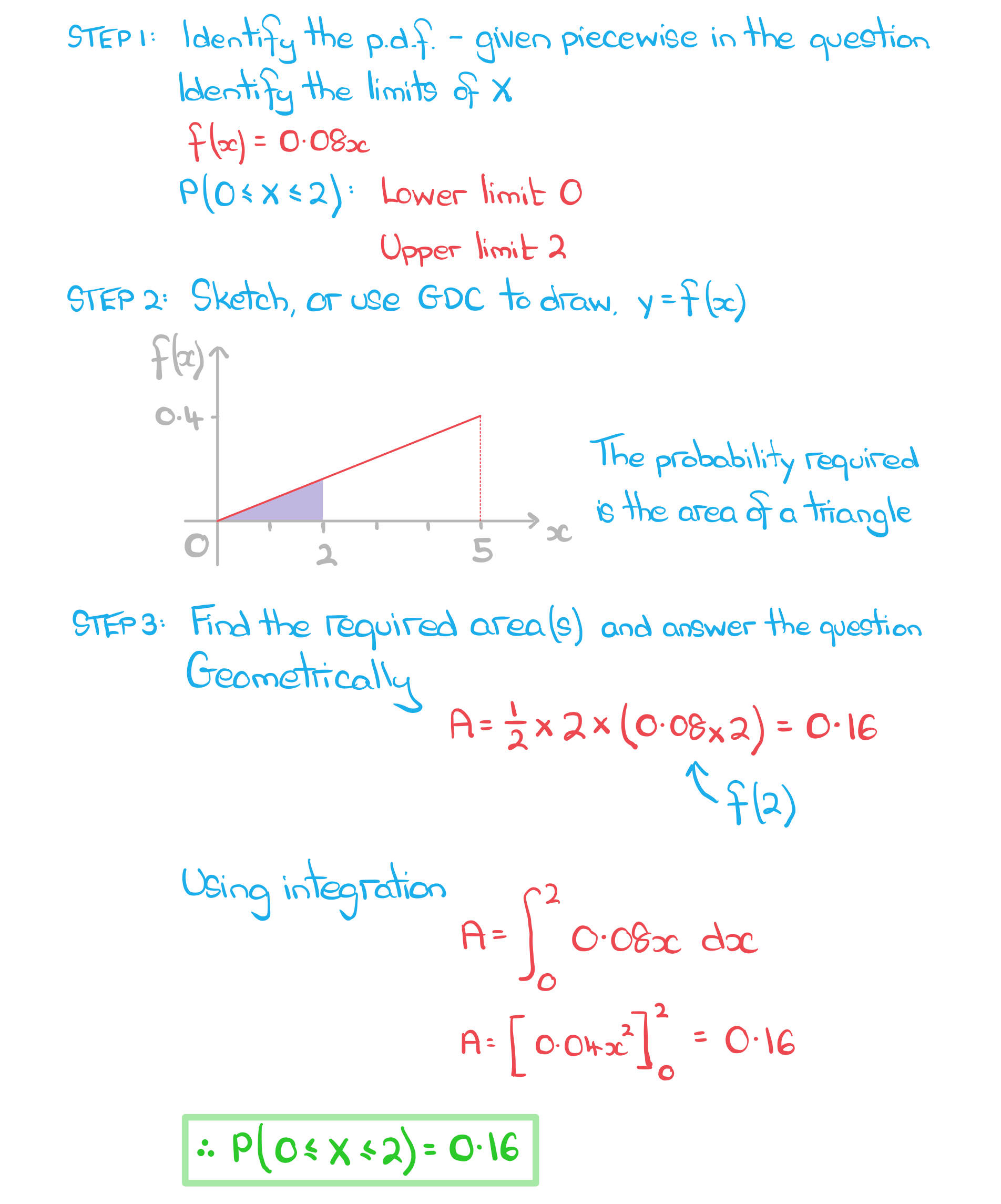
STEP 1
Identify the probability density function, f(x) - this may be given as a graph, an equation or as a piecewise function
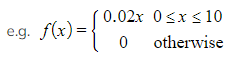 Identify the limits of X for a particular problem
Identify the limits of X for a particular problemRemember that P(a ≤ X ≤ b) = P(a < X < b)
STEP 2
Sketch, or use your GDC to draw, the graph of y = f(x)
Look for basic shapes (rectangles, triangles and trapezoids) as finding these areas is easier without using integration
Look for symmetry in the graph that may make the problem easier
Break the area required into two or more parts if it makes the problem easier
Look for basic shapes (rectangles, triangles and trapezoids) as finding these areas is easier without using integration
Look for symmetry in the graph that may make the problem easier
Break the area required into two or more parts if it makes the problem easier
STEP 3
Find the area(s) required using basic shapes or integration and answer the question
- Trickier problems may involve finding a limit of the integral given its value
- i.e. Find one of the boundaries in the domain of X, given the probability
- e.g. Find the value of a given that P(0 ≤ X ≤ a) = 0.09
- i.e. Find one of the boundaries in the domain of X, given the probability
Worked Example
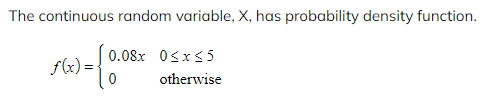 a) Show that f(x) can represent a probability density function.
a) Show that f(x) can represent a probability density function.
b) Find, both geometrically and using integration, P(0 ≤ X ≤ 2).
c) Write down P(X = 3.2).
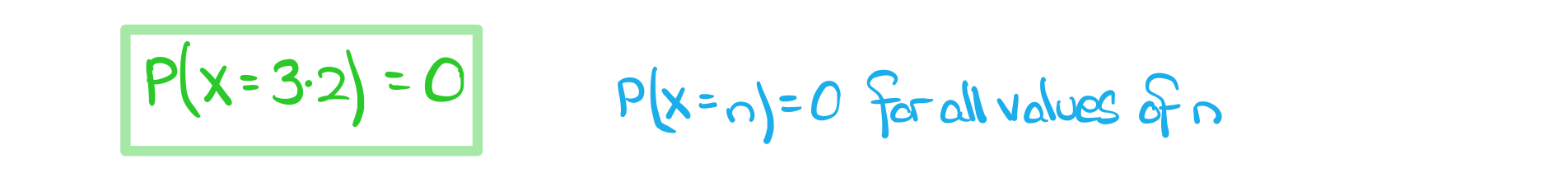
Median & Mode of a CRV
What is meant by the median of a continuous random variable?
 IF the p.d.f. is symmetrical (i.e. the graph of y = f(x) is symmetrical) then the median will be halfway between the lower and upper limits of x
IF the p.d.f. is symmetrical (i.e. the graph of y = f(x) is symmetrical) then the median will be halfway between the lower and upper limits of x
- In such cases the graph of y = f(x) has axis of symmetry in the line x = m
How do I find the median of a continuous random variable?
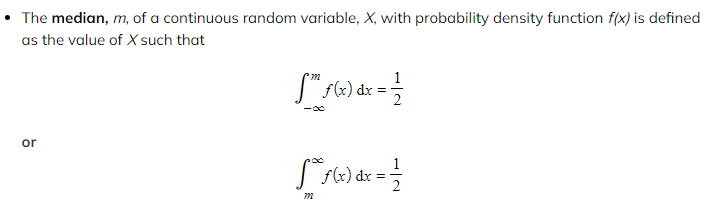 The equation that should be used will depend on the information in the question
The equation that should be used will depend on the information in the question
- If the graph of y = f(x) is symmetrical, symmetry may be used to deduce the median
- This may often be the case if f(x) is linear and the area under the graph is a basic shape such as a rectangle
How do I find the median of a continuous random variable with a piecewise p.d.f.?
- For piecewise functions, the location of the median will determine which equation to use in order to find it
- For example
 What is meant by the mode of a continuous random variable?
What is meant by the mode of a continuous random variable?
- The mode of a continuous random variable, X, with probability density function f(x) is the value of x that produces the greatest value of f(x)
How do I find the mode of a continuous random variable?
- This will depend on the type of function f(x); the easiest way to find the mode is by considering the shape of the graph of y = f(x)
- If the graph is a curve with a maximum point, the mode can be found by differentiating and solving f’(x) = 0
- If there is more than one solution to f’(x) = 0 then further work may be needed in deducing the mode
- There could be more than one mode
- Look for valid values of x from the domain of the p.d.f.
- Use the second derivative (f’’(x)) to deduce the nature of each stationary point
- Check the values of f(x) at the lower and upper limits of x, one of these could be the maximum value f(x) reaches
- If there is more than one solution to f’(x) = 0 then further work may be needed in deducing the mode
- If the graph of y = f(x) is symmetrical, symmetry may be used to deduce the mode
- For a symmetrical p.d.f., median = mode = mean
Worked Example
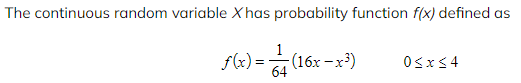 a) Find the median of X, giving your answer to three significant figures.
a) Find the median of X, giving your answer to three significant figures.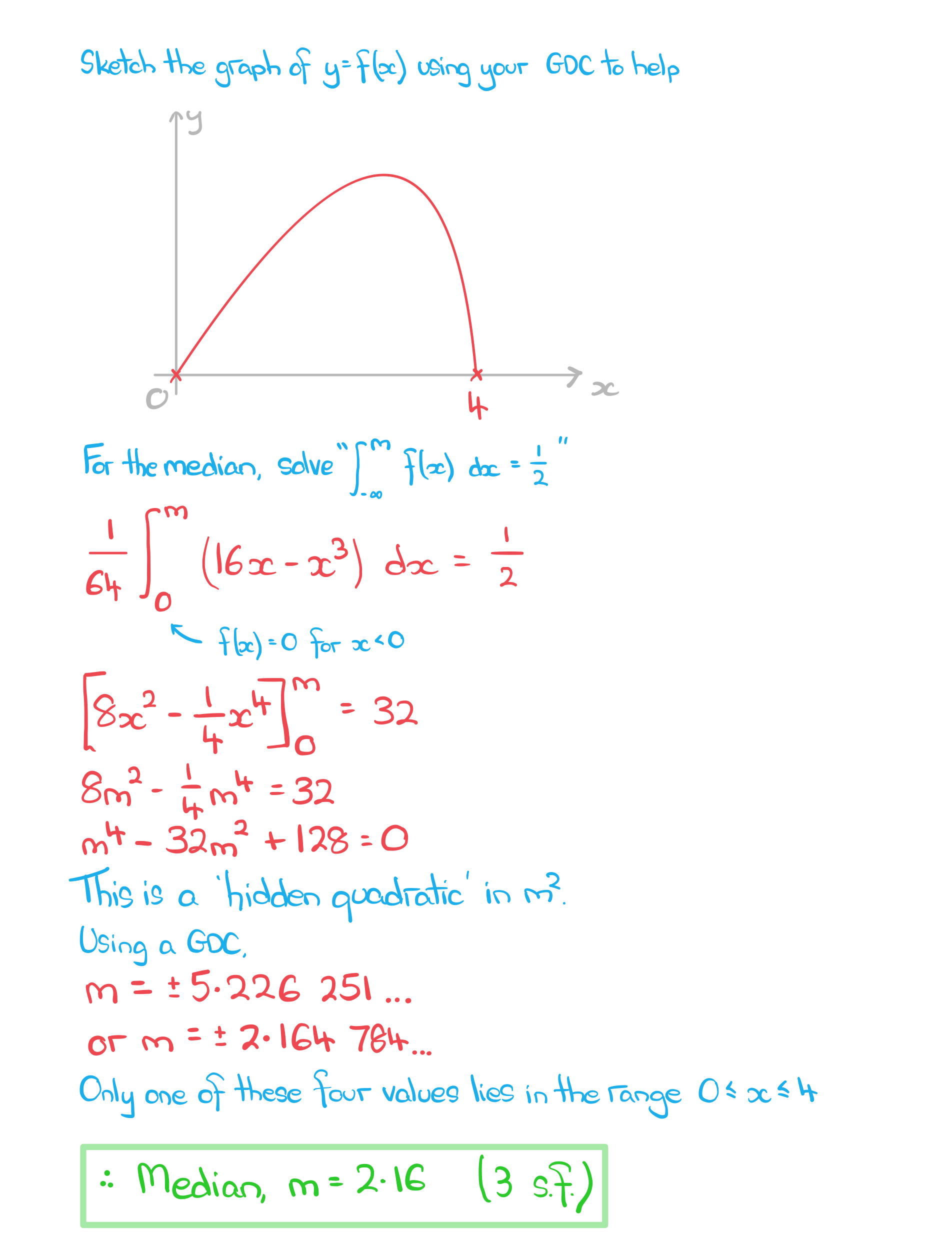
b) Find the exact value of the mode of X.

Mean & Variance of a CRV
What are the mean and variance of a continuous random variable?
- E(X) is the expected value, or mean, of the continuous random variable X
- E(X) can also be denoted by μ
- Var(X) is the variance of the continuous random variable X
- Var(X) can also be denoted by σ2
- The standard deviation, σ, is the square root of the variance
How do I find the mean and variance of a continuous random variable?
 How do I find the mean and variance of a linear transformation of a continuous random variable?
How do I find the mean and variance of a linear transformation of a continuous random variable?
- For the continuous random variable, X, with mean E(X) and variance Var(X) then
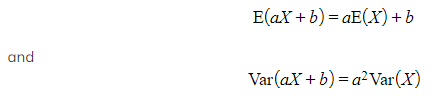 Exam Tip
Exam Tip
- Using your GDC to draw the graph of y = f(x) can highlight any symmetrical properties which reduce the work involved in finding the mean and variance
Worked Example
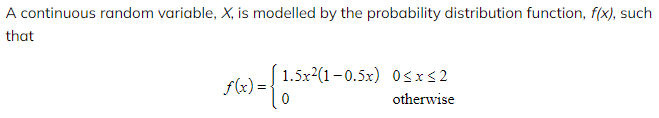 a) Find the mean of X.
a) Find the mean of X.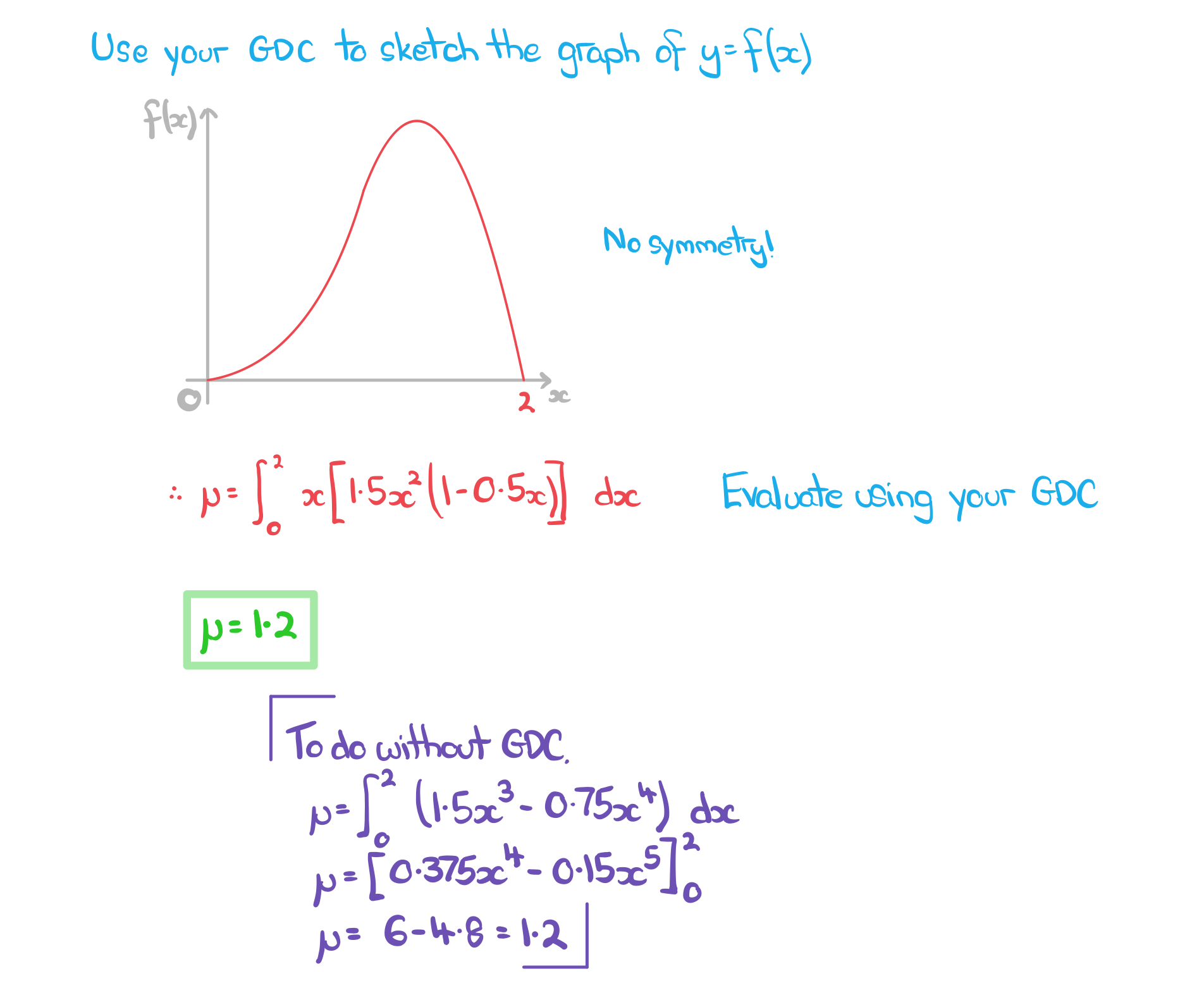
b) Find standard deviation of X.
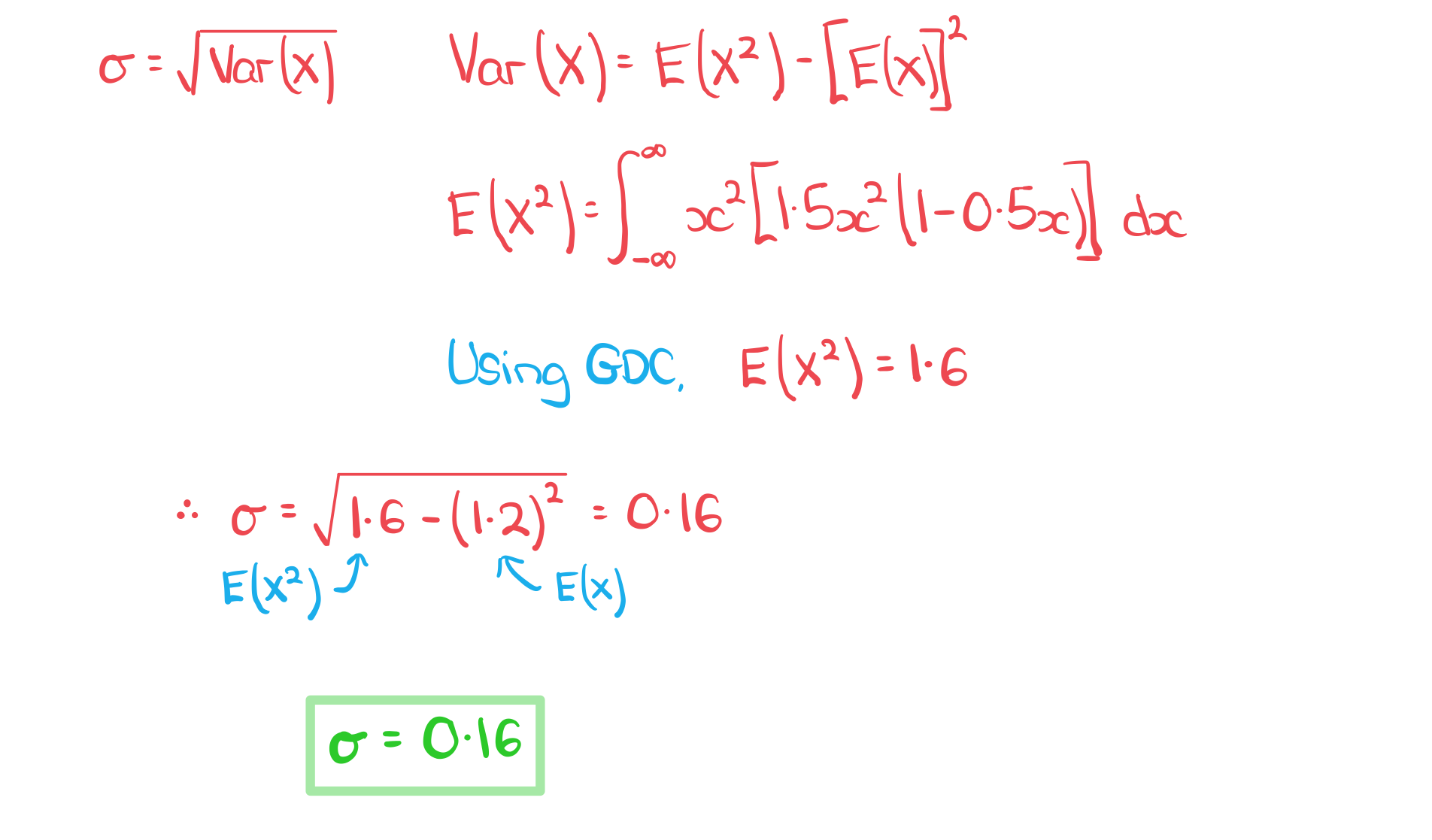
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









