- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel IGCSE Biology 复习笔记 2.7.1 Diffusion in Gas Exchange
Edexcel IGCSE Biology 复习笔记 2.7.1 Diffusion in Gas Exchange
Diffusion in Gas Exchange
- Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a region of its higher concentration to a region of its lower concentration
- Molecules move down a concentration gradient, as a result of their random movement
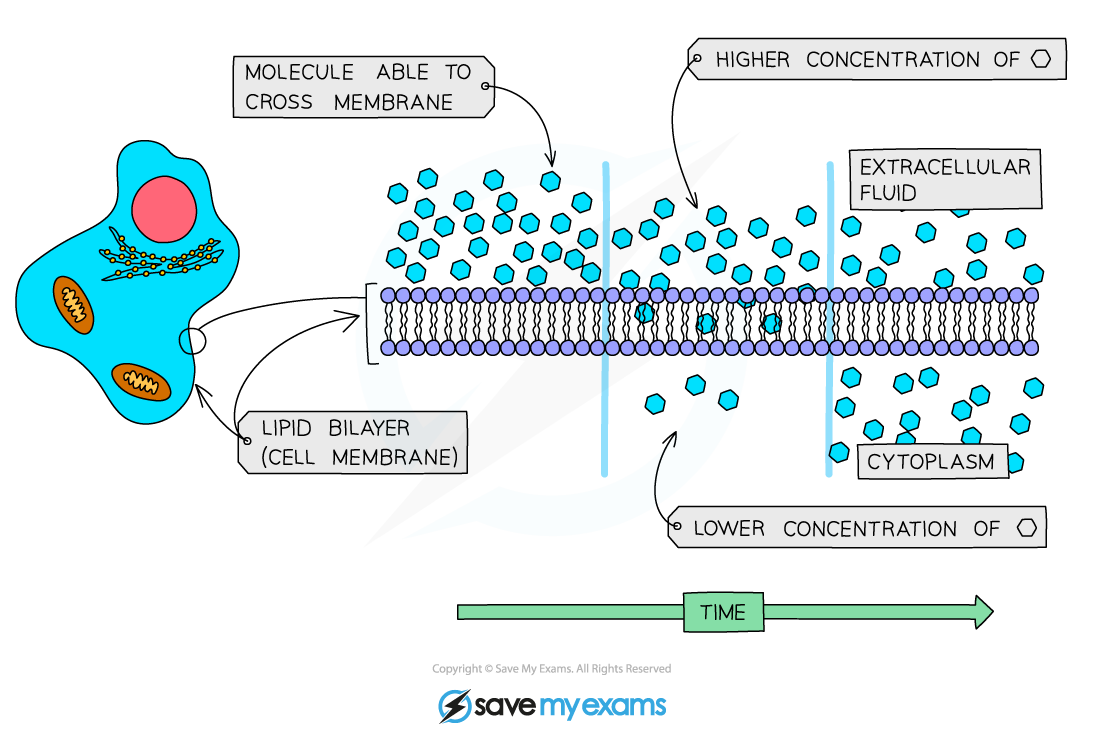
Diffusion across the cell membrane
- Diffusion is the process by which gas exchange occurs
- Single celled organisms, such as amoeba, can exchange gases sufficiently by simple diffusion through the cell membrane
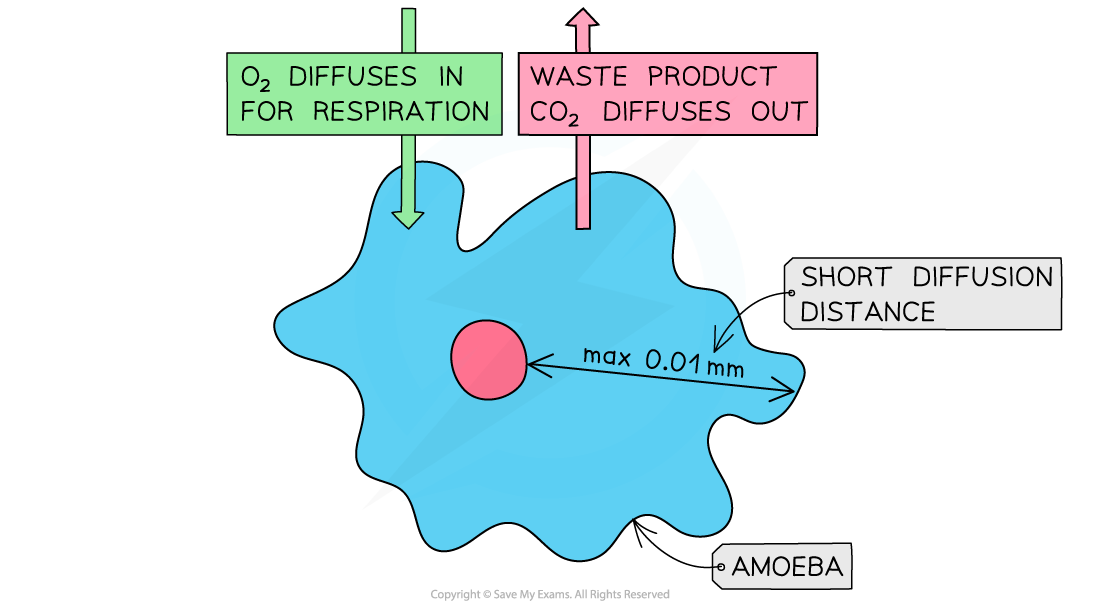
Gas exchange in single-celled organisms (such as amoeba) occurs through diffusion
- Multicellular organisms (such as plants and animals), however, have exchange surfaces and organ systems that maximise the exchange of materials
- Gills are the gas exchange organs in fish, lungs in humans and leaves or roots in plants
- These organs increase the efficiency of exchange in a number of ways:
- Having a large surface area to increase the rate of transport
- A short diffusion distance for substances to move across. This short distance is created because the barrier that separates two regions is as thin as possible
- In addition, animals have:
- Gas exchange surfaces that are well ventilated to maintain steep concentration gradients
转载自savemyexam

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









