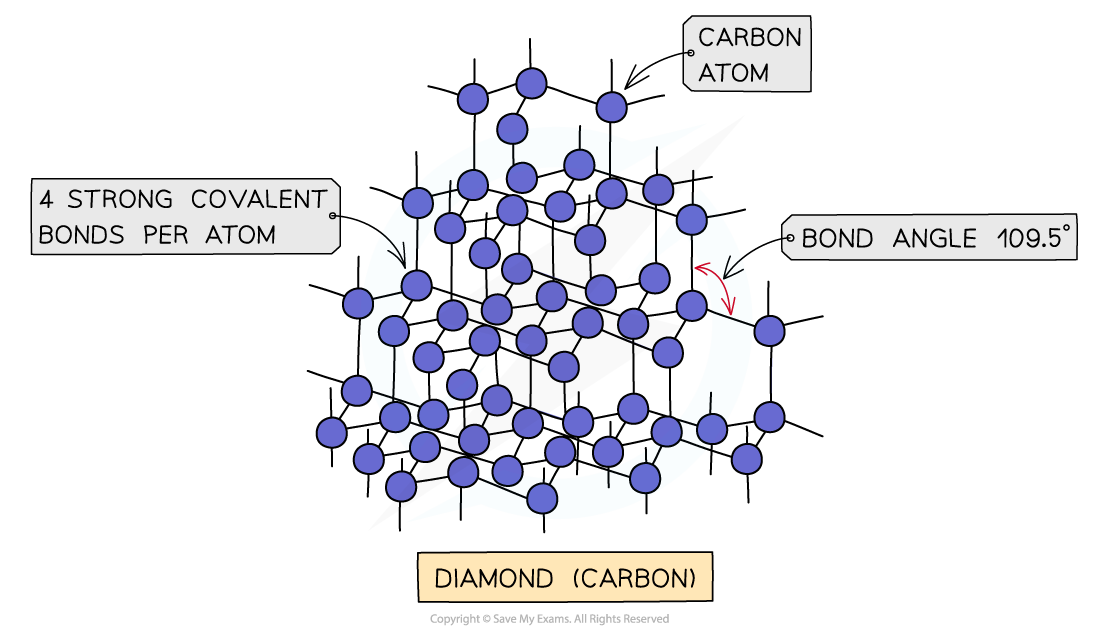
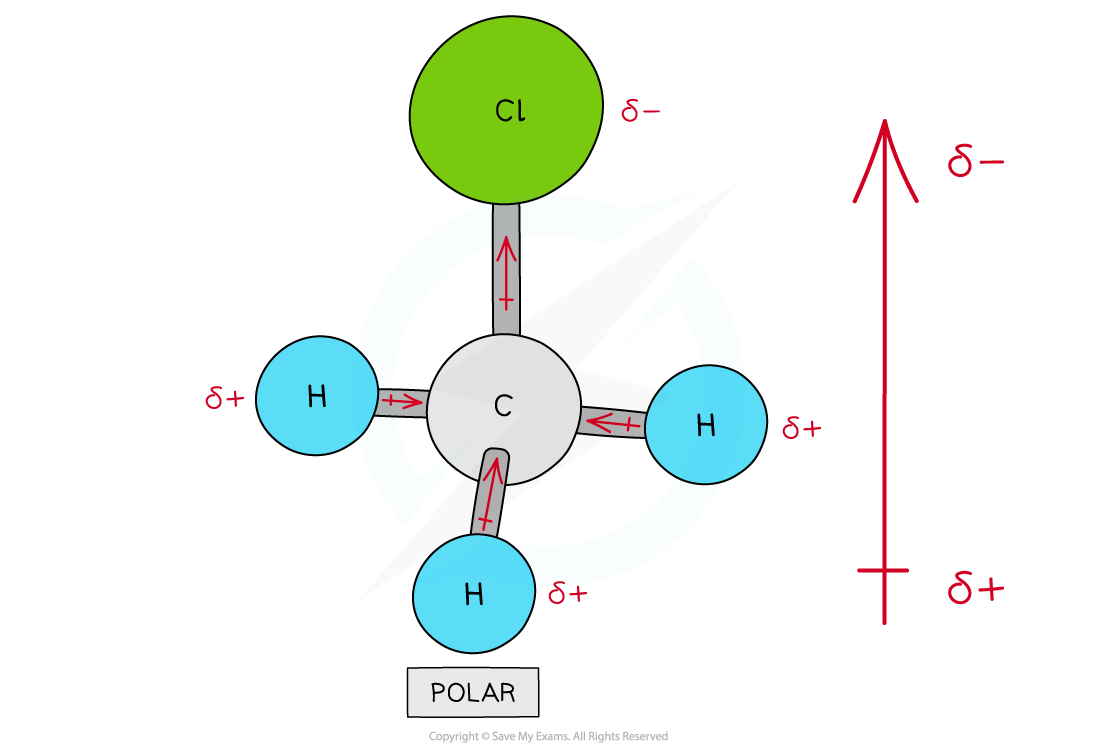
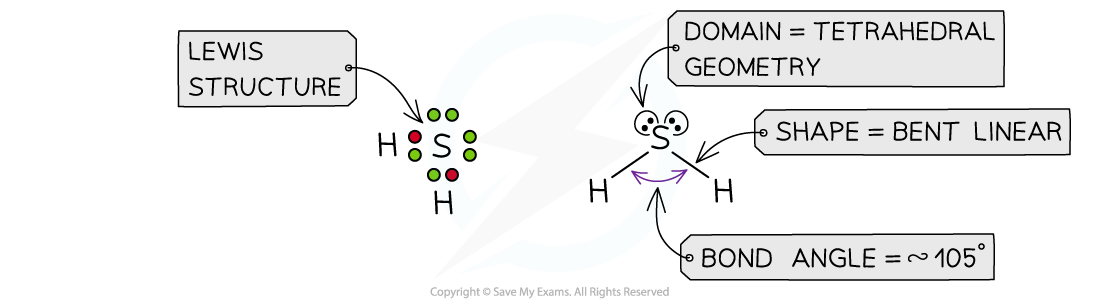
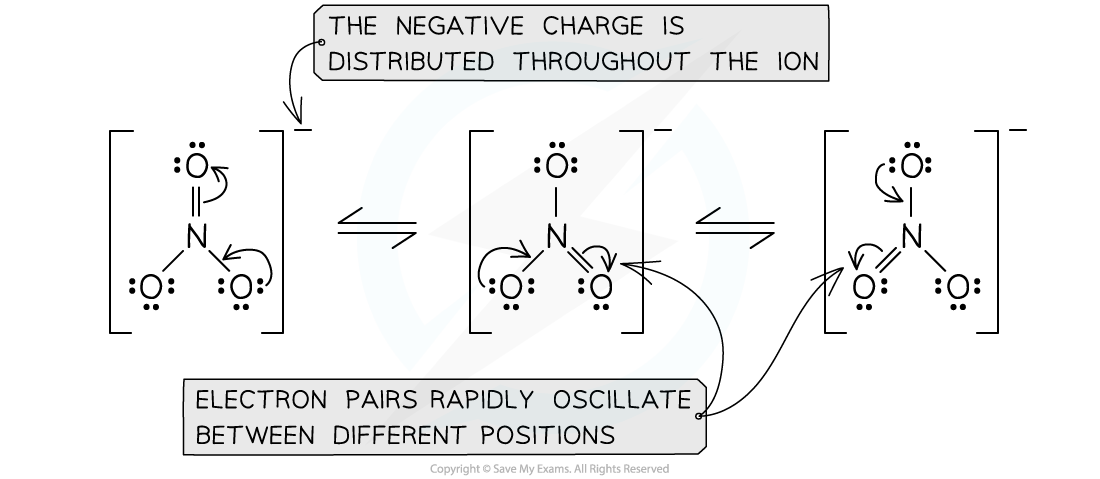
IB DP Chemistry: HL复习笔记4.3.2 Deducing Intermolecular Forces
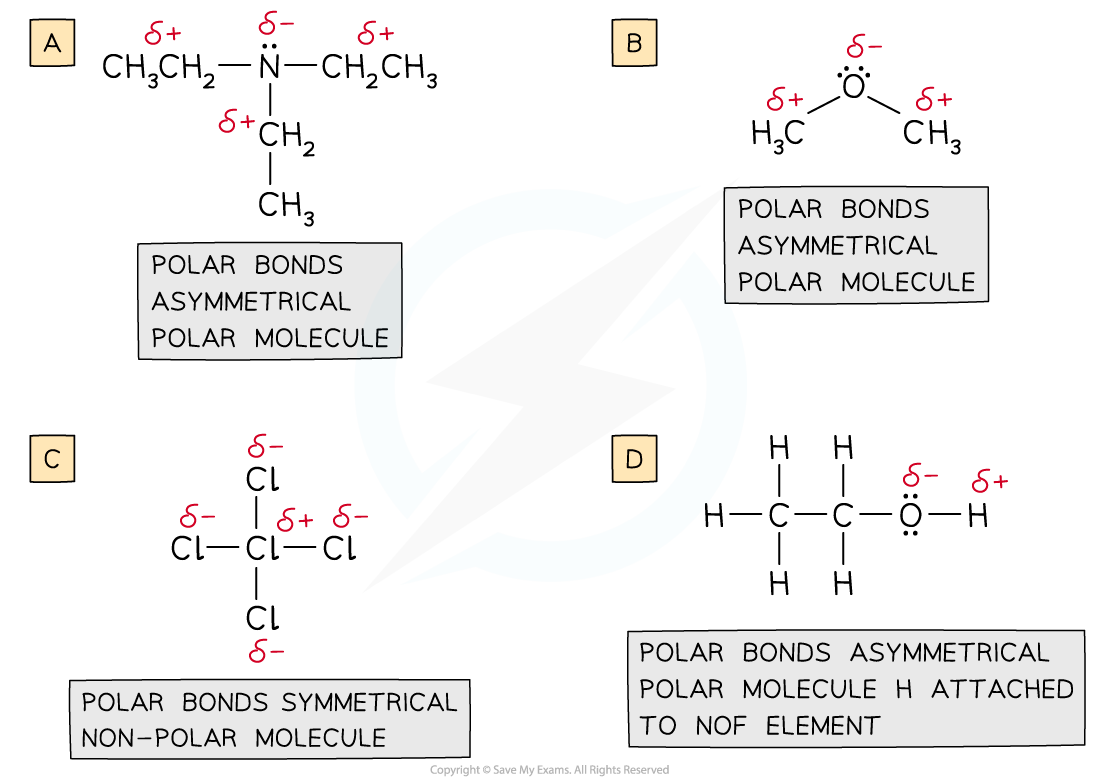
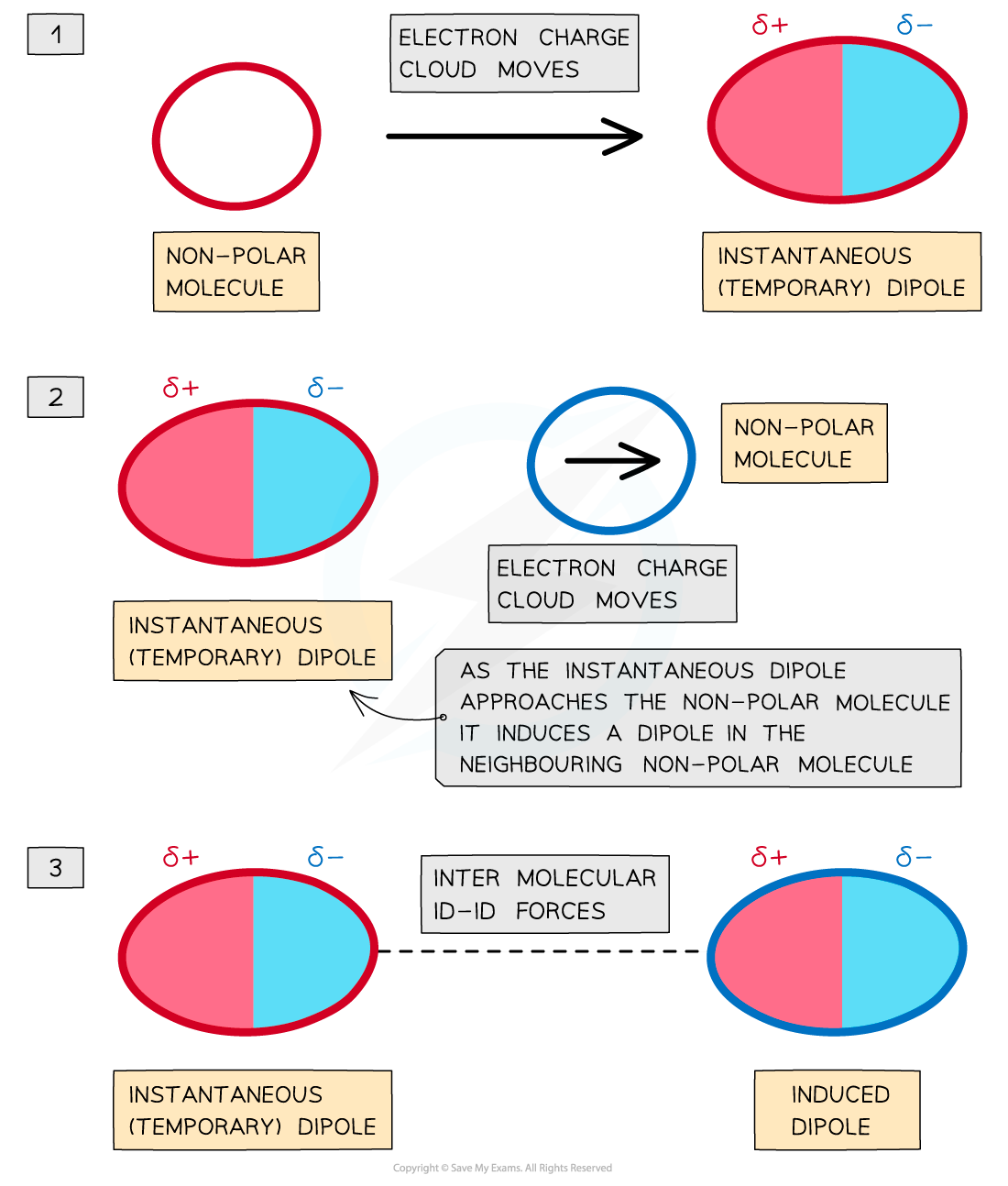
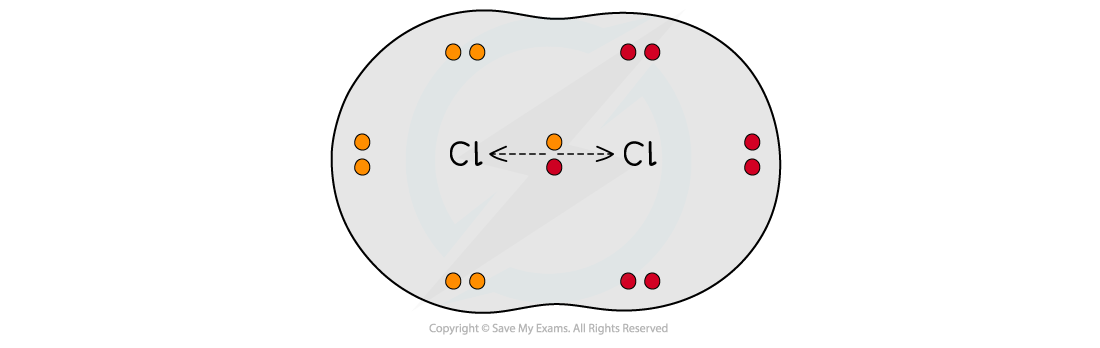
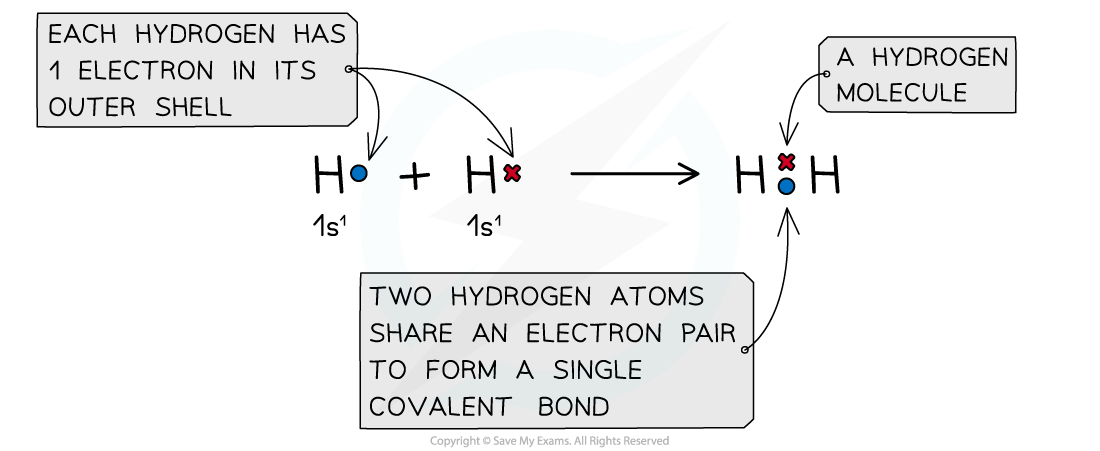
Deducing Intermolecular Forces In order to deduce the types of intermolecular forces present in molecules you need information about the structure and chemical formula of the molecules The chemical...