- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel A Level Economics A:复习笔记3.4.4 Oligopoly
Characteristics of Oligopoly
- Most markets are imperfectly competitive
- Most imperfectly competitive industries operate in an oligopoly market structure
- E.g., Banks, insurance companies, department stores, supermarkets, petrol retailers, sport stores etc.
Characteristics Of an Oligopoly Market
| High barriers to entry and exit | High concentration ratio |
|
|
| Interdependence of firms | Product differentiation |
|
|
Calculation of Concentration Ratios
- The most commonly used concentration ratios in the UK are the five-firm, ten-firm, & twenty-firm concentration ratios
- A five-firm concentration ratio of around 60% is considered to be an oligopoly
- A one-firm concentration ratio of 100% would be a pure monopoly
- The UK Competition Commission defines a monopoly as a firm with more than 25% market share
- It prevents mergers or acquisitions from taking place which would give one firm more than 25% market share
- The UK Competition Commission defines a monopoly as a firm with more than 25% market share
Worked Example
The following table shows the value of UK Supermarket sales for the 3 months to the 31st March 2022.
| Company | Value of Sales (£ million) |
| Tesco | 136.5 |
| Morrisons | 55 |
| The Co-operative | 30 |
| Sainsbury's | 75 |
| Aldi | 44 |
| Waitrose | 24 |
| Asda | 77.5 |
| Lidl | 33 |
| Iceland | 15 |
| Others | 10 |
| 500 |
Calculate the five-firm concentration ratio. Show your working.
Step 1: Identify the top five firms by value of sales & add the value of their sales together
Tesco (136.5) + Asda (77.5) + Sainsbury's (75) + Morrisons (55) + Aldi (44)
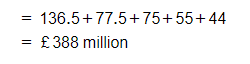
Step 2: Calculate the percentage of total sales that the top five firms have
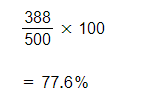
Reasons For Collusive & Non-collusive Behaviour
- Collusive behaviour in oligopolies occurs when firms cooperate to fix prices & restrict output
- They cease to compete as vigorously as they can
- Non collusive behaviour in oligopolies occurs when firms actively compete to maintain/increase market share
Reasons For Collusion
| Few firms/competitors | This makes it relatively easy for each firm to understand other competitors' actions & responses, or to collaborate on prices/output |
| Similar costs | Firms face almost identical costs as any remaining competitors have all experienced economies of scale |
| Similar revenue | Competitors' goods/services sell for similar prices as there is little incentive to lower them as other firms would respond by keeping their market share the same but decreasing the profits |
| High barriers to entry | The barriers to entry make it unlikely that new entrants will emerge to disrupt the status quo |
| Ineffective regulation | A lack of regulation empowers firms to collude as there is little consequence for their actions |
| Brand loyalty | There is usually a high degree of brand loyalty in oligopoly markets & firms have an established market share. This decreases the benefits of competition as consumers are unlikely to change brands |
Types of Collusion
- Collusion can be overt or tacit
- The net effect of collusion is that a group of firms end up acting more like a monopoly in the market
- Overt collusion occurs when firms explicitly agree to limit competition or raise prices (price fixing)
- A cartel is the most restrictive form of collusion & is illegal in most countries
- The consequences of overt collusion include:
- Higher prices for consumers
- Less output in the market
- Poor quality products and/or customer service
- Less investment in innovation
- Overt collusion often happens in the following ways
- Price fixing
- Setting output quotas which limit supply & naturally results in price increases
- Agreements to block new firms from entering the industry
- Agreements to pay suppliers the same price thereby driving down prices in the supply chain (monopsony power)
- Tacit collusion occurs when firms avoid formal agreements but closely monitor each other's behaviour usually following the lead of the largest firm in the industry
-
- The most common form of tacit collusion is price leadership
- This occurs when firms monitor the price of the largest firm in the industry & then adjust their prices to match
- It is difficult for regulators to prove that collusion has occurred
- It provides similar benefits to firms as overt collusion, but perhaps not to the same degree
- It has similar consequences for consumers as overt collusion, but perhaps not to the same degree
- The most common form of tacit collusion is price leadership
Game Theory
- Game theory is a mathematical framework which is used by firms to ensure optimal decisions are made in a strategic setting where there is a high level of interdependence (such as in oligopoly markets)
- Any game has three elements
- The players - (firms)
- The strategies available to the players
- The payoffs (outcomes) that each player receives for each combination of strategies
- It was first illustrated using a simple model called The Prisoners Dilemma
- Two criminals are caught after a train robbery (Carol & Doug)
- The prosecutor does not have much evidence
- The criminals are guilty but have agreed with each other that they will deny all involvement
- The prosector wants one (or both) to confess
- The strategies & payoffs available to the prisoners are presented in a payoff matrix
- Two criminals are caught after a train robbery (Carol & Doug)
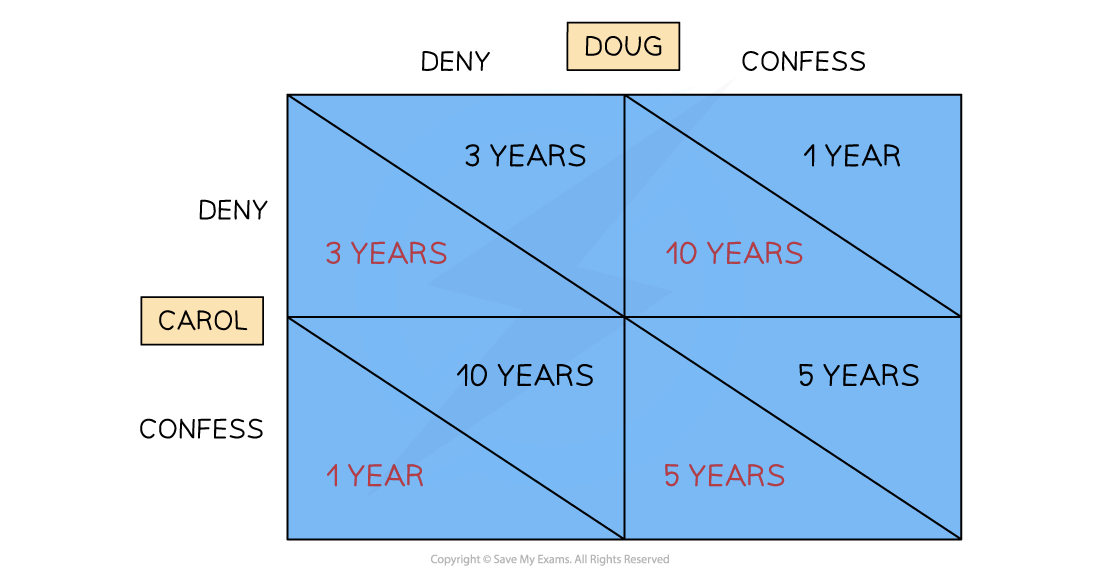
A prisoner's dilemma payoff matrix which illustrates game theory
Diagram Analysis
- If Carol & Doug stick to their plan & deny involvement, they each get 3 years jail time
- If Doug confesses & indicates Carol's involvement, then Doug gets a lenient sentence of 1 year & Carol gets 10 years
- If Carol confesses & indicates Doug's involvement, then Carol gets a lenient sentence of 1 year & Doug gets 10 years
- There is a strong incentive to collude as it will yield the most beneficial outcome for Carol and Doug (3 years each)
- Fearing the worst, both players decide to confess and receive 5 years each
- This outcome is called the dominant strategy as it carries the least risk
How Firms Use Game Theory
- Firms typically use game theory in the following situations:
- When making decisions to raise or lower prices
- When making decisions about new advertising & branding initiatives
- When making decisions about investment in product innovation
- When making decisions on product bundling e.g. combined phone & broadband packages
- Below is a payoff matrix representing the strategic options available to Burger King & McDonald's when making advertising decisions
- The £ payoffs represent the likely profits for each combination of choices selected
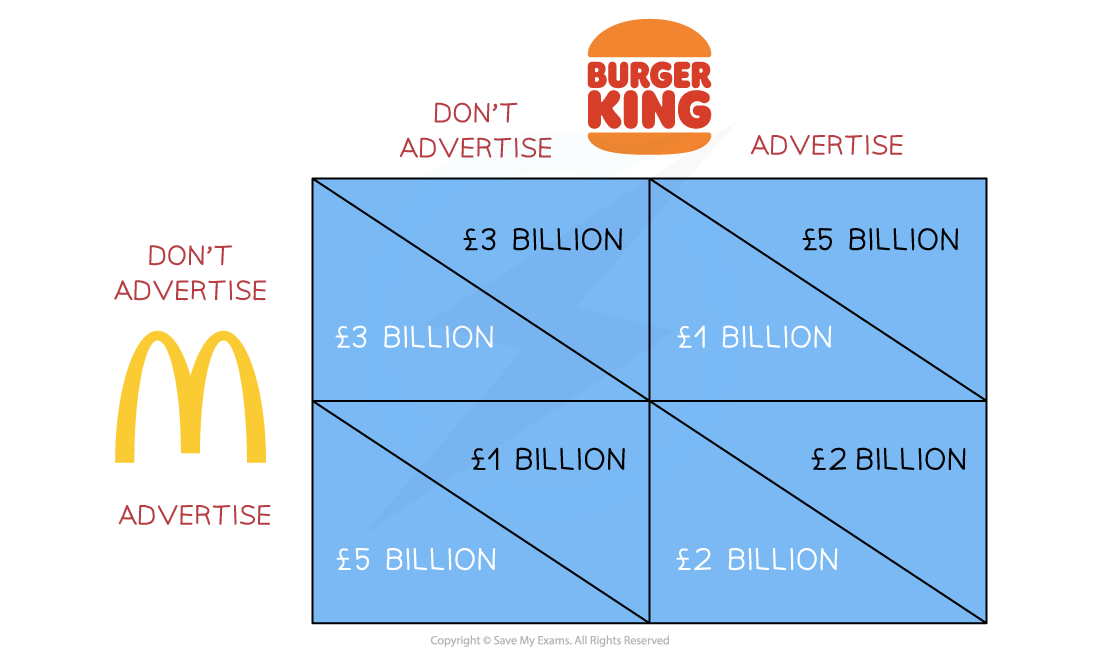
A payoff matrix which illustrates the strategies & payoffs available to firms when they are deciding to advertise or not to advertise
Diagram Analysis
- If Burger King & McDonald's collude & agree not to advertise (top left), they can each enjoy £3 bn. in profits
- There is a strong incentive to collude
- If Burger King advertises & McDonald's does not, then Burger King's profits are £5 bn. & McDonald's are £1 bn.
- If McDonald's advertises & Burger King does not, then McDonald's profits are £5 bn. & Burger King's are £1 bn.
- Both firms decide to advertise & receive £2 bn. of profits each
- This outcome is called the dominant strategy as it carries the least risk
- The risk of collusion is that one player will cheat and by doing so, get ahead
Worked Example
The grid below shows the possible pricing strategies of two coffee companies. The Bean and Black Gold. Assuming that demand is price inelastic.
| The Bean's price |
| High | Low | ||
| Black Gold's price | High | A | B |
| Low | C | D |
Which of the following strategies in the grid would maximise the revenue of the two firms? Explain your answer.
Step 1: Use the information provided to select the correct option
A
Step 2: Explain your answer using economic knowledge
With reference to the revenue rule, firms whose demand is price inelastic should raise their price to maximise revenue. Due to the fact that consumers consider coffee a necessity, they will continue to pay the high prices. However, there is a strong likelihood that firms will charge a low price (D) as the payoff matrix carries the lowest risk. If firms do collusively or non-collusively decide to charge the high price, then B & C represent higher revenue for any firm that first decides to lower their price (their market share will increase)
Price Competition
- Firms in an oligopoly market engage in three types of price competition
- Price wars: occur when competitors repeatedly lower prices to undercut each other in an attempt to gain or increase market share. This often occurs when there is a lower level of non-price competition & where firms find it difficult to collude (either formal or tacit)
- Predatory pricing: this is the practice of lowering prices when a new competitor joins the industry in order to drive them out. Prices are often lowered to a point below the cost of production. Once they have left the market, prices are raised again. This pricing strategy is usually illegal as it is anticompetitive
- Limit pricing: occurs when firms set a limit on how high the price will go in the industry. A lower price reduces profit & disincentivize other firms from joining the industry. The greater the barriers to entry the higher the limit price is likely to be as firms are already disincentivized
Types of Non-price Competition
- Firms engage in a wide range of non-price competition strategies
- The aim is to increase product differentiation, develop or increase brand loyalty, & to increase market share
A Range of Strategies Used in Non-Price Competition
| Loyalty cards & rewards | Branding | Packaging | Celebrity/influencer endorsement |
| Corporate sponsorship e.g. Nike sponsoring Rafael Nadal | After sales service | Delivery policies | Product warranties |
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









