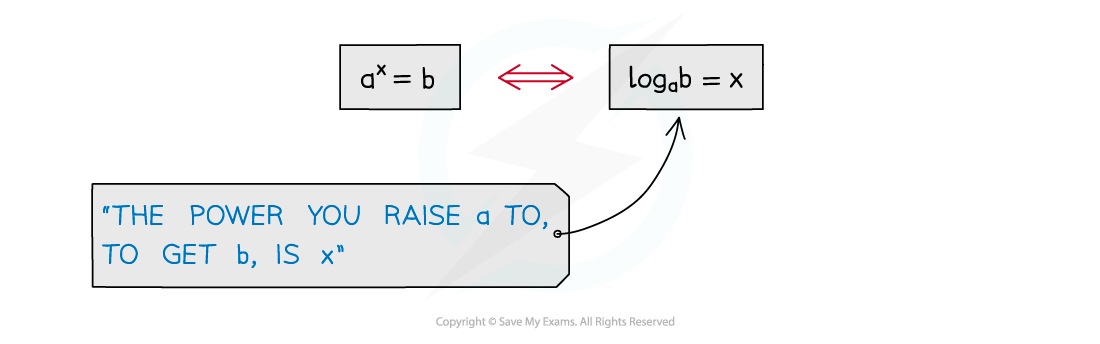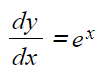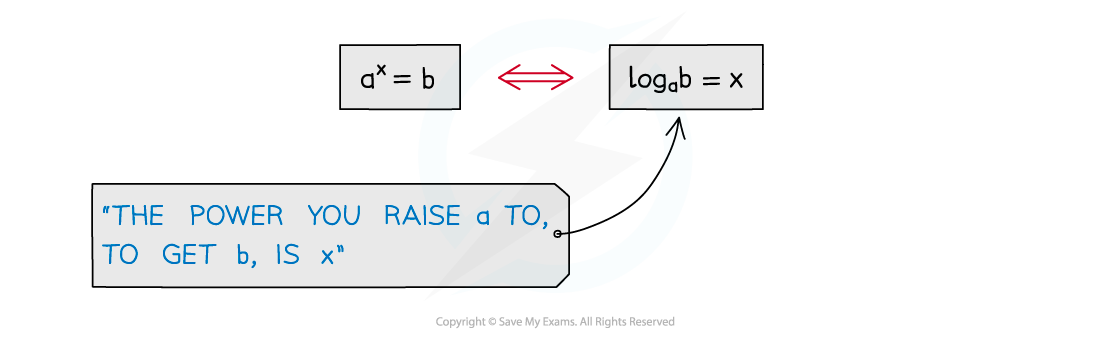AQA A Level Maths: Pure复习笔记6.3.3 Using Log Graphs in Modelling
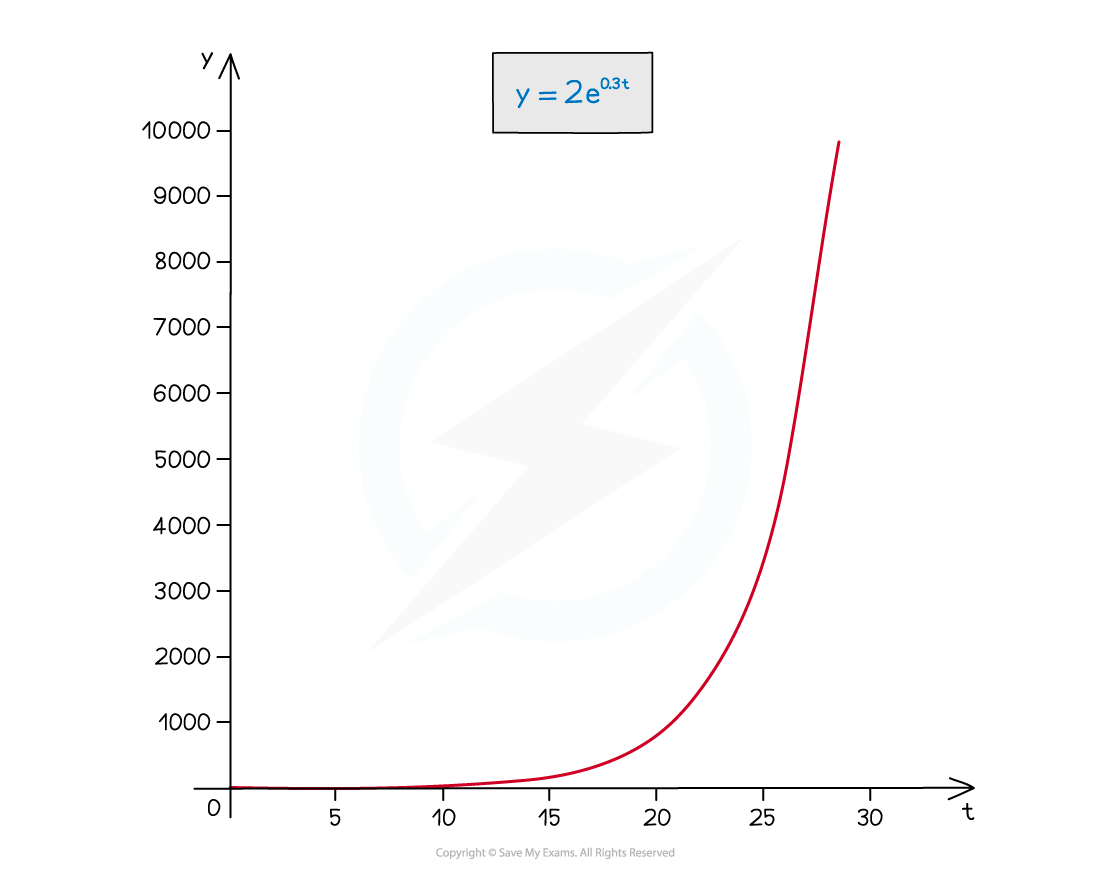
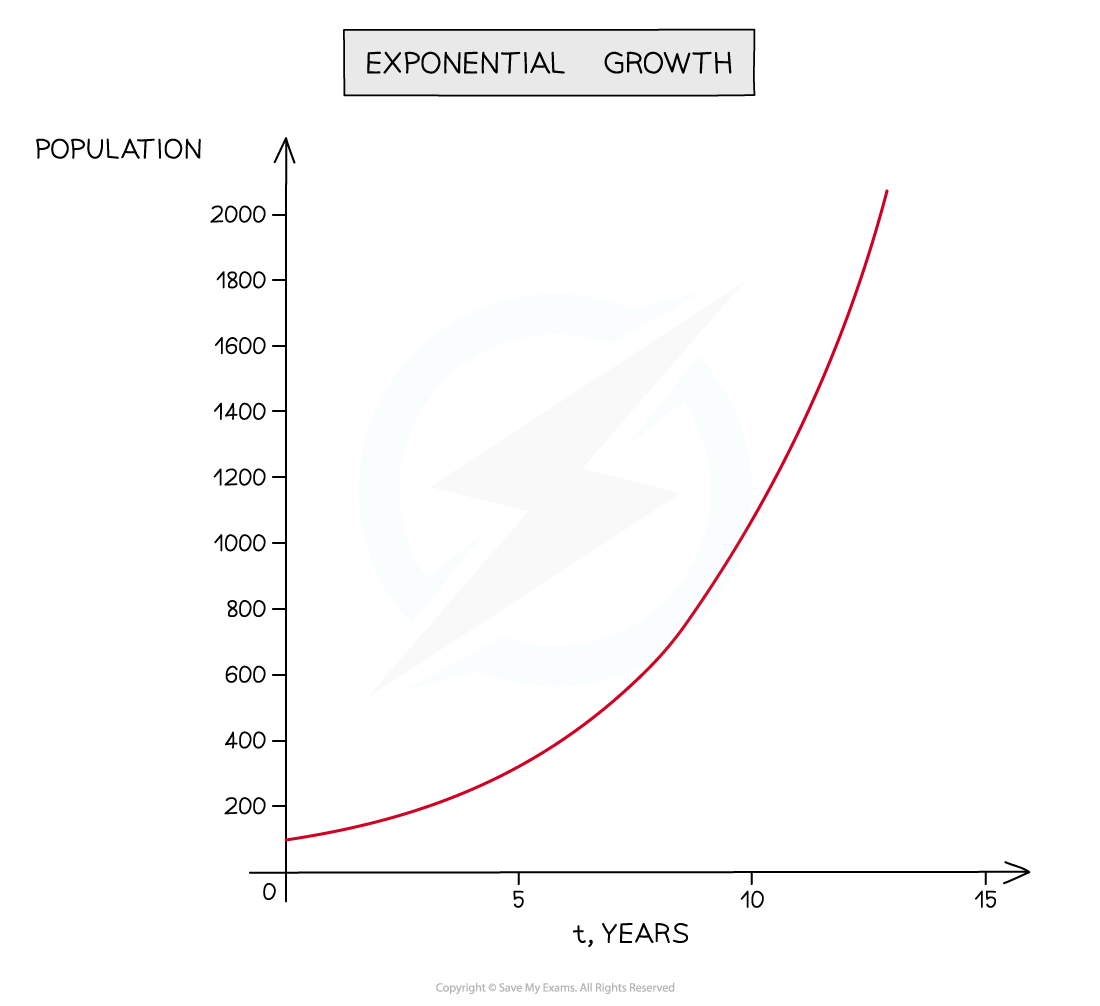
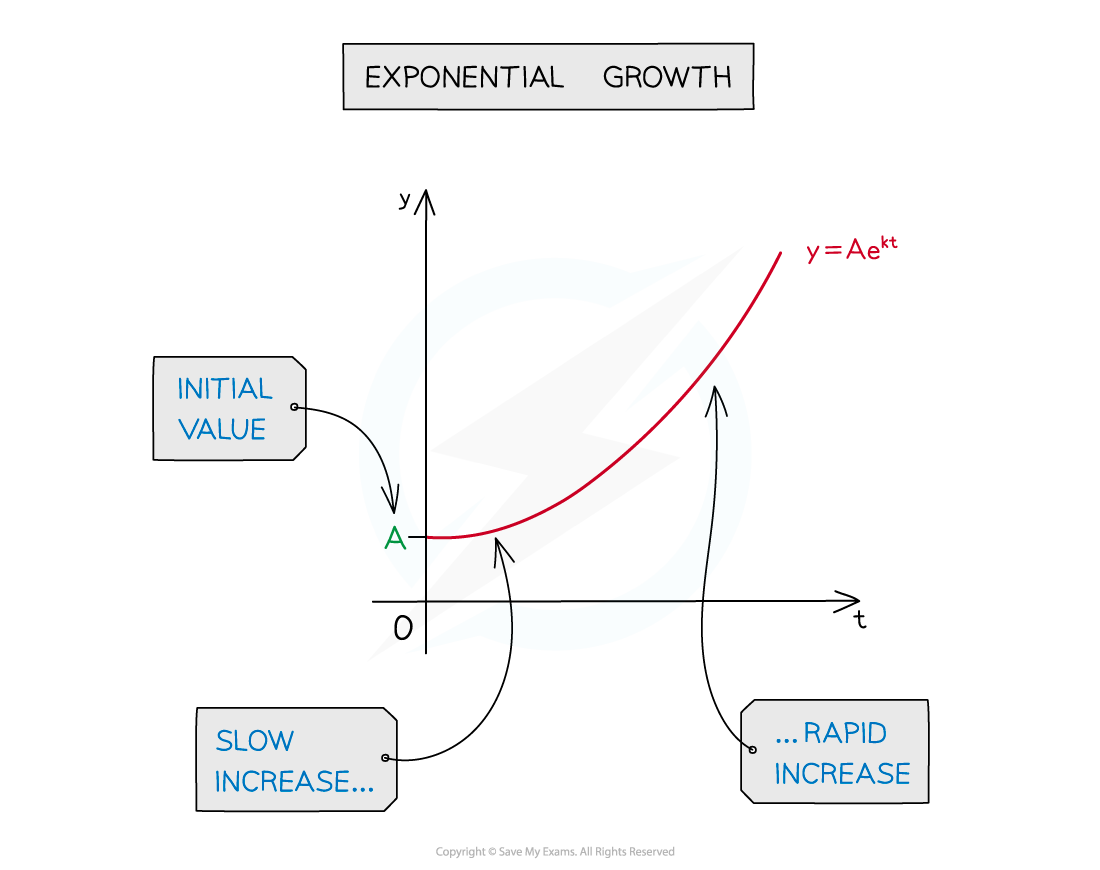
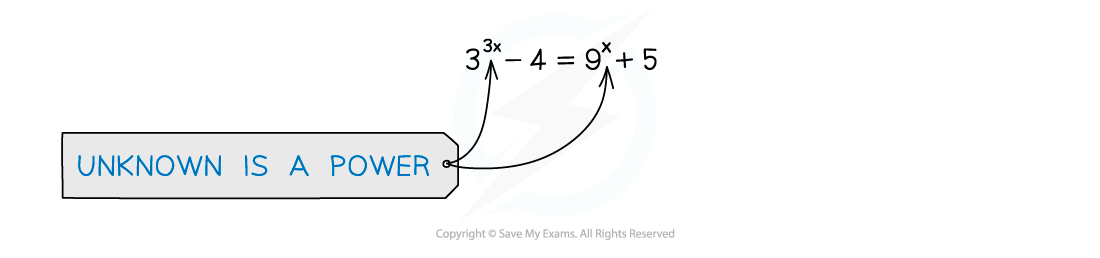
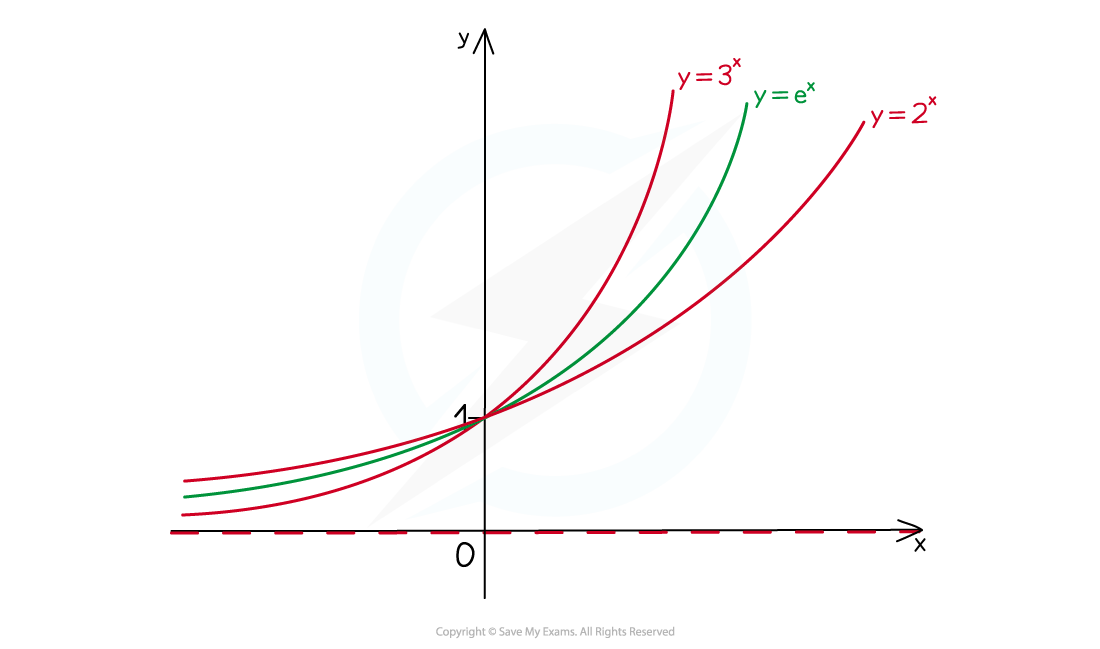
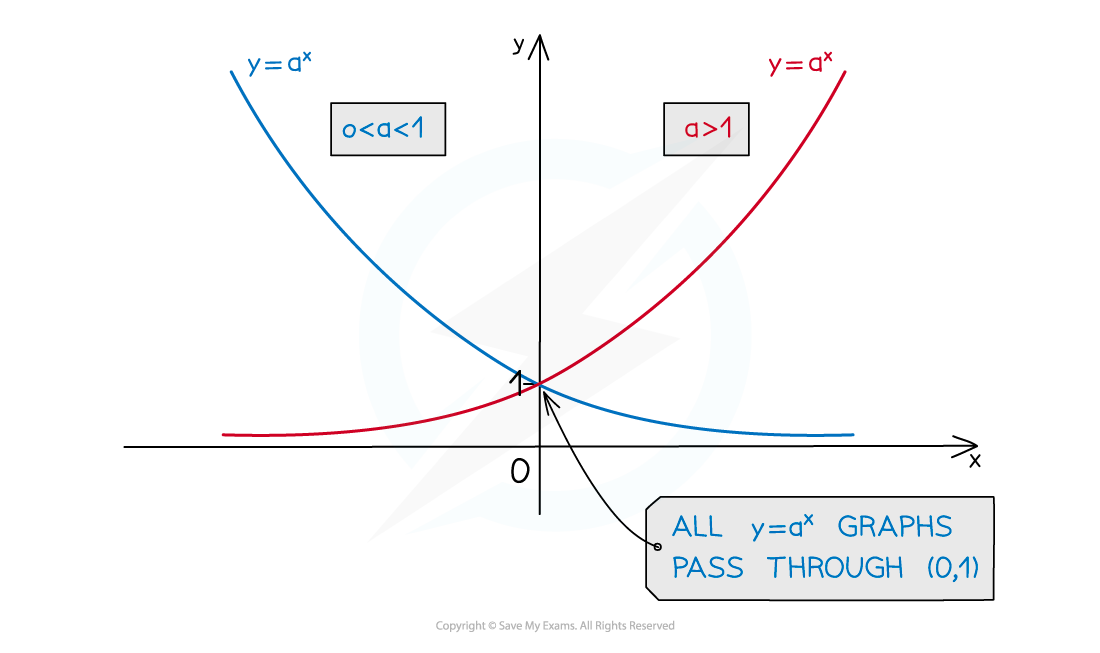
Using Log Graphs in Modelling What are log graphs? Log graphs are used when the scale of a graph increases or decreases exponentially It can very difficult to read specific values from graphs with ...